
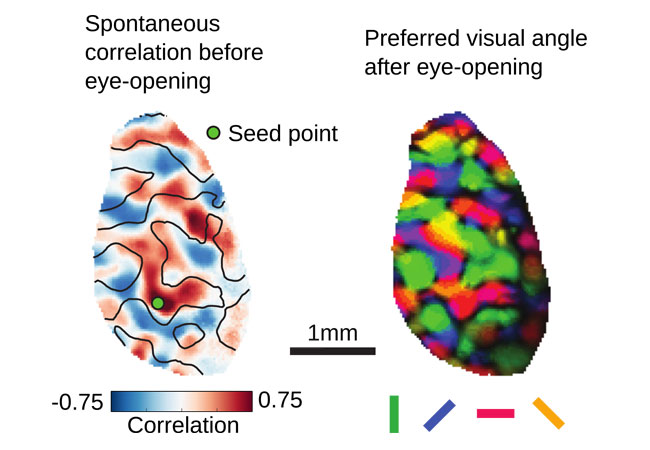
Spatial patterns of spontaneous correlation (example in figure on the left) in the immature visual cortex prior to eye-opening are distributed across several millimeters and resemble the layout of the response properties (example on the right) of visual cortex after eye-opening.
One of the outstanding mysteries of the cerebral cortex is how individual neurons develop the proper synaptic connections to form large-scale, distributed networks. Now, an international team of scientists including researchers from Goethe University and the FIAS have gained novel insights from spontaneously generated patterns of activity by local networks in the early developing visual cortex. Apparently these form the basis for long-range neural connections that are established through brain activity over the course of cortical development.
Now, as published in Nature Neuroscience, scientists at the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies, Goethe University of Frankfurt, and the University of Minnesota have investigated the visual cortex of the ferret, an ideal model system to explore the early development of networks in the cortex.
These are composed of thousands of neurons and are distributed over millimetres of the cortical surface. In the visual cortex, network activity encodes specific features of the visual scene like the orientation of edges and the direction of object motion.
By using calcium imaging techniques, the scientists were able to visualize with unprecedented resolution spontaneous activity patterns, i.e. patterns not produced by visual input. To their great surprise, the spontaneous activity patterns were highly correlated between distant populations of neurons – and in fact were so highly correlated that the activity of small populations of neurons could reliably predict coincident network activity patterns millimetres away, and these correlation patterns beautifully predicted the patterns of network activity evoked by visual stimulation.
In their next step, the researchers used this remarkable correspondence of spontaneous and visually-evoked network patterns to find out how the interaction of networks developed in the immature brain.
By looking at the state of spontaneous activity patterns prior to eye opening, they expected to see a striking difference in the patterns of spontaneous activity because the long-range cortical connections that are thought to be the basis for distributed network activity patterns are absent in the immature cortex.
To their surprise, they discovered robust long-range patterns of correlated spontaneous activity prior to eye opening, and found that they extended over distances comparable to what was seen in the mature brain.
Confronted with this paradox, the researchers first considered whether the correlated activity patterns could be spreading through chains of local cortical connections, similar to a forest fire. To test this intriguing possibility, Matthias Kaschube, Professor for Computer Science at Goethe University and Fellow at the Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies (FIAS), and his doctoral student Bettina Hein, built a computational model of the neural circuitry in the early visual cortex.
They found that by using a set of parameters that are consistent with the organization of local cortical connections, the model could precisely reproduce the patterns of spontaneous long-range correlations they had observed experimentally, without the need for long-range connections.
Taken together, these results suggest that long-range order in the early developing cortex originates from neural activity driven by short-range connections. In other words, local connections build a network activity scaffold. Following the well-accepted plasticity rule ‘what fires together wires together’, activity mediated by local connections can then guide the subsequent formation of long-range network connections. In a twist of the oft-used phrase, ‘think globally, act locally’, developing cortical circuits act locally to achieve global effects. Future studies will test the prediction that activity dependent plasticity mechanisms shape the structure of long-range connections based on the instructive activity patterns derived from local cortical connections.
Publication:
Gordon B Smith, Bettina Hein, Dave E Whitney, David Fitzpatrick, Matthias Kaschube: Distributed network interactions and their emergence in developing neocortex (2018) Nature Neuroscience. http://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-018-0247-5
An image to download can be found here: www.uni-frankfurt.de/74522335
Caption: Spatial patterns of spontaneous correlation (example in figure on the left) in the immature visual cortex prior to eye-opening are distributed across several millimeters and resemble the layout of the response properties (example on the right) of visual cortex after eye-opening.
Credit: Bettina Hein
Further information: Professor Matthias Kaschube, Institute for Computer Science and Frankfurt Institute for Applied Sciences, Riedberg Campus, Tel. +49 69 798-47521, kaschube@fias.uni-frankfurt.de.
Current news about science, teaching, and society in GOETHE-UNI online (www.aktuelles.uni-frankfurt.de)
Goethe University is a research-oriented university in the European financial centre Frankfurt The university was founded in 1914 through private funding, primarily from Jewish sponsors, and has since produced pioneering achievements in the areas of social sciences, sociology and economics, medicine, quantum physics, brain research, and labour law. It gained a unique level of autonomy on 1 January 2008 by returning to its historic roots as a “foundation university”. Today, it is among the top ten in external funding and among the top three largest universities in Germany, with three clusters of excellence in medicine, life sciences and the humanities. Together with the Technical University of Darmstadt and the University of Mainz, it acts as a partner of the inter-state strategic Rhine-Main University Alliance. Internet: www.uni-frankfurt.de
Publisher: The President of Goethe University Editor: Dr. Anne Hardy, Referee for Science Communication, PR & Communication Department, Theodor-W.-Adorno-Platz 1, 60323 Frankfurt am Main, Tel: (069) 798-13035, Fax: (069) 798-763 12531.
Professor Matthias Kaschube, Institute for Computer Science and Frankfurt Institute for Applied Sciences, Riedberg Campus, Tel. +49 69 798-47521, kaschube@fias.uni-frankfurt.de.
Gordon B Smith, Bettina Hein, Dave E Whitney, David Fitzpatrick, Matthias Kaschube: Distributed network interactions and their emergence in developing neocortex (2018) Nature Neuroscience. http://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-018-0247-5












