
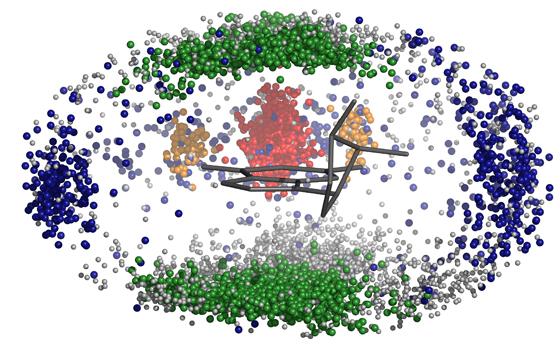
This image shows a three-dimensional distribution of nucleobases obtained from the crystal structure of a ribosomal RNA molecule. Different colours correspond to the different interaction types: Watson-Crick pairs in red/orange, non-canonical interactions in blue, stacked pairs in green.
Credit: SISSA
Messenger, transfer, ribosomal… there's more than one type of RNA. The difference lies not only in the sequence of the nucleotides, the “beads” that form the strand, but also in the three-dimensional structure that this long molecule takes on.
Computer models are often used to reveal this structure but these tend to be rather complex, and they vary depending on the field of application. A team of SISSA scientists used numerical techniques to develop a new “geometrical” model which has the advantage of being much simpler and faster than those traditionally used as well as having cross-sectional applications to different fields of study. The method proved to be effective and robust in the tests.
RNA, just like DNA, is a long chain composed of nucleotides, the building blocks that contain nucleobases, the “letters” that encode the information contained in these molecules. “It's relatively easy to discover the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule using standard experimental techniques”, explains Giovanni Bussi, a professor at SISSA. “What's more difficult is to discover the shape of the molecule, but this is often crucial if we want to understand its function”.
The method devised by Bussi and colleagues has the advantage of being based on very simple rules, and it has shown to be less cumbersome than the other computational methods currently used in laboratories. “Our technique looks at the relative position of nucleotides, their geometry, and, on this basis, it is able to classify the molecules according to their structure”.
“We ran a series of tests on the method” comments Sandro Bottaro of SISSA and first author of the paper published in the scientific journal Nucleic Acid Research. “For example, we constructed a scoring function. In practice, having to compare different possible predictions of RNA structure, the scoring function provides a measure of the accuracy of each prediction. There are many ways to do this depending on the field of application. We assessed the reliability of our method, finding that it performed as well as and, in some cases, even better than conventional methods, which are, however, considerably more complex”.
This means that, as well as being simpler than average, the method is also more versatile as it can be applied to a broad range of problems. In addition to Bussi and Bottaro, Francesco di Palma, a SISSA student, also took part in the study.















