Transcriptional mechanisms governing cartilage formation
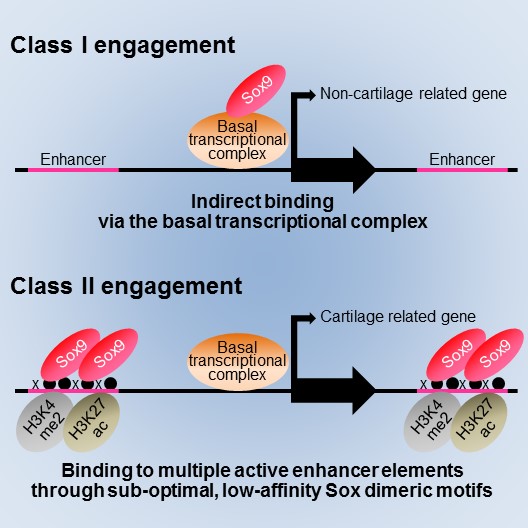
Model for two distinct modes of Sox9 action in cartilage formation proposed in the present study. In Class I engagement, Sox9 binds to the genome indirectly via the basal transcriptional complex, regulating transcription of genes for basal cell activities. In Class II engagement, Sox9 binds to multiple active enhancer elements through sub-optimal, low-affinity Sox dimeric motifs (DNA sequences), resulting in a high level of transcription of cartilage-related genes. © 2015 Shinsuke Ohba.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have identified modes of Sox9 action during cartilage formation by analyzing big data on Sox9 location, chromatin state, and gene expression over the whole mouse genome.
This finding will contribute to the understanding of cartilage diseases caused by genomic mutation and genome-based drug discovery for disease therapies.
Cartilage generated in embryos not only regulates skeletal growth until puberty, but also plays a key role in our locomotion as articular cartilage in our joints. Cartilage formation (chondrogenesis) requires the normal function of Sox9, a protein that regulates the expression of chondrogenesis-related genes.
Mutation around the region of the human SOX9 gene, which encodes the Sox9 protein, causes campomelic dysplasia, a congenital disease that is accompanied by skeletal abnormalities and other conditions.
Although the mechanisms underlying Sox9-mediated transcriptional regulation during chondrogenesis have been intensively investigated at a certain genomic region, its genome-wide regulation remained unclear.
Project Associate Professor Shinsuke Ohba at the Department of Bioengineering, the University of Tokyo Graduate School of Engineering, identified two genome-wide modes (Class I and Class II engagement) of Sox9 action in transcription during chondrogenesis.
In Class I engagement, Sox9 binds indirectly to the DNA and regulates the transcription of genes involved in basal cell activities. In Class II engagement, it binds directly to the DNA in multiple locations and activates transcription of cartilage-related genes.
“This finding will contribute to the understanding of cartilage-related degenerative diseases and congenital abnormalities that are caused by genomic mutation and genome-based drug discovery for treatment of diseases and cartilage regeneration,” says Ohba.
This work was published in the online version of Cell Reports (Cell Press) on July 2, 2015. This research was carried out in collaboration with Professor Andrew P. McMahon at the University of Southern California.
Paper
Shinsuke Ohba, Xinjun He, Hironori Hojo, Andrew P. McMahon, “Distinct transcriptional programs underlie Sox9 regulation of the mammalian chondrocyte”, Cell Reports Online Edition: 2015/7/3 (Japan time), doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.013.
Associated links
U Tokyo Research article
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.researchsea.comAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



