Two are better than one – another checkpoint enzyme for flawless cell division
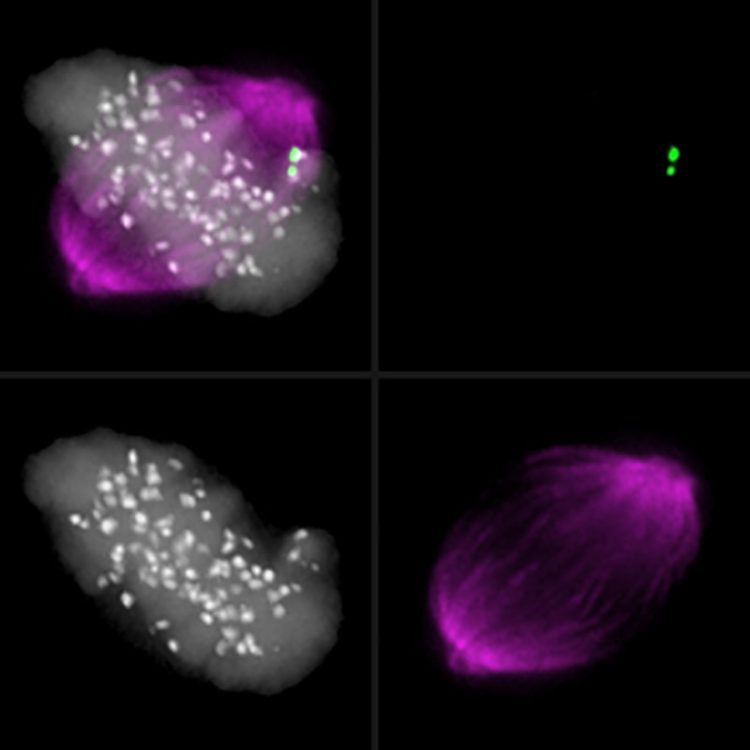
Mitotic spindle apparatus preparing for chromosome segregation: an unaligned chromosome activates the checkpoint (green) and thereby prevents premature segregation. © University of Basel, Biozentrum
Each day, the cells of the human body divide billions of times; this also requires duplication of their genetic information. Errors in cell division can cause tumor formation, and an exact segregation of the DNA (chromosomes) is therefore essential to ensure the health of the whole organism.
Prof. Erich Nigg’s research group at the Biozentrum, University of Basel, has demonstrated that the enzyme Plk1 plays a significant role in monitoring the segregation of chromosomes.
Plk1 has checkpoint function
The segregation of the 23 chromosome pairs of human cells only occurs when all parameters are correct. This is ensured by a surveillance process, a so-called checkpoint. Central to this checkpoint is an inhibitor formed on the chromosomes, called mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), which prevents cell division until all settings on the mitotic spindle, the chromosome segregation apparatus, are correct.
“Just like the enzyme Mps1, Plk1 also ensures the assembly of the MCC and finally the inhibition of cell division,” says the first author Conrad von Schubert. “Plk1 thus also has a checkpoint function and consequently safeguards chromosome segregation.”
In the past, various functions have been attributed to the enzyme Plk1, including the correct assembly and disassembly of the mitotic spindle. “The newly uncovered checkpoint function of Plk1 had been overlooked, however, since other functions obscured this phenomenon,” explains Conrad von Schubert.
The research team could now demonstrate that Plk1 influences the inhibitor MCC via at least two pathways. In a nutshell, Plk1 supports the enzyme Mps1, whose checkpoint function had already been known for some time. “Plk1 ensures rapid and robust checkpoint activation by acting in a similar way to Mps1, thus reinforcing Mps1 activity,” says Conrad von Schubert.
Plk1 demonstrates evolutionary stability
“While Plk1 and Mps1 cooperate in human cells, Plk1 has prevailed over Mps1 during the evolution of other organisms,” remarks Conrad von Schubert. Because Mps1 has disappeared in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, Plk1 has taken over the entire checkpoint function in this organism, as shown by an independent study in the same issue of the journal.
Combined drugs against cancer?
Mps1 is currently being investigated as a possible target for the treatment of cancer. “However, the fact that Plk1 also exhibits checkpoint function during cell division was not known,” says Conrad von Schubert. The new findings suggest that both enzymes should be considered as targets for cancer therapy. “Drugs against Plk1 were developed some time ago and, in light of our findings, it would be interesting to test the potential of a combinatorial treatment.”
Original article
Conrad von Schubert, Fabien Cubizolles, Jasmine M. Bracher, Tale Sliedrecht, Geert J.P.L. Kops, and Erich A. Nigg
Plk1 and Mps1 Cooperatively Regulate the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint in Human Cells
Cell Reports, published online June 25, 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.007
Further Information
Prof. Dr. Erich Nigg, University of Basel, Biozentrum, phone: +41 61 267 16 56, email: erich.nigg@unibas.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



