
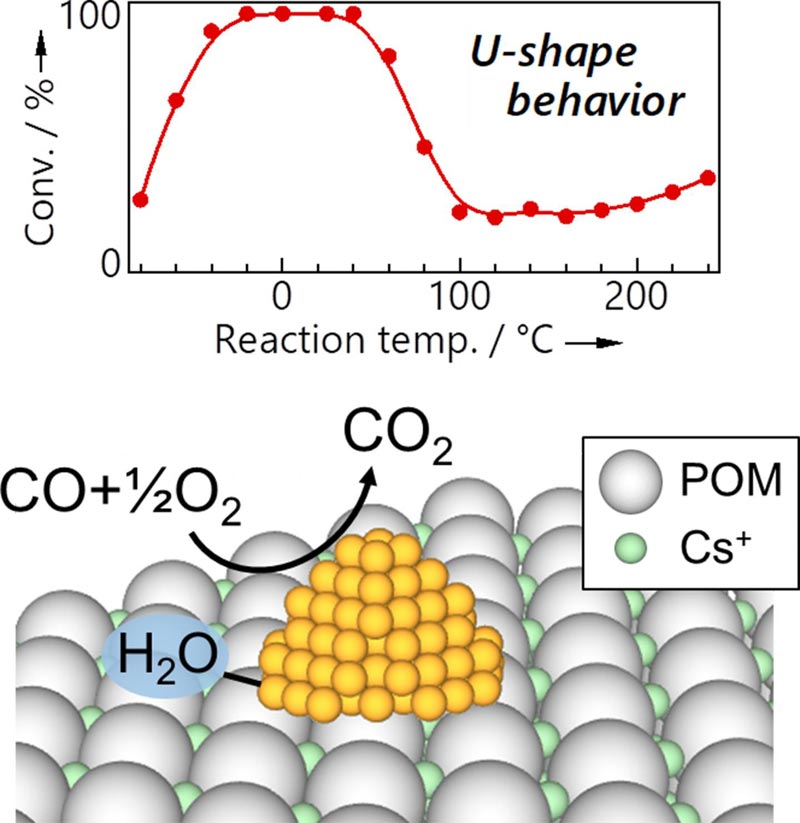
New catalyst consisting of gold nanoparticles supported on a Keggin-type polyoxometalate (POM) with a cesium salt. The structure showed high activity and stability for CO oxidation; trace amounts of water were found to be essential to the function of the material. Catalytic activity showed a unique, U-shaped dependence on temperature.
Credit: Toru Murayama
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to mount gold nanoparticles on a molecular support known as a polyoxometalate (POM). They successfully applied this to realize nearly 100% conversion of carbon monoxide (CO) over a wide temperature range, demonstrating stable performance over long periods of time.
They showed how traces of water uniquely contribute to the catalyst's function, promising insight into catalysis and potential application to exhaust gas and room air purification.
Gas purification is an extremely important industrial process, whether in factories, catalytic converters for vehicle exhausts, or the domestic air purifier. Recently, research has focused on using nanometer-sized gold particles, prized for their ability to speed up (“catalyze”) chemical reactions, even at very small (<5 nm) sizes. These often need to be mounted on a solid “support”.
The research group of Toru Murayama (Project Professor) and Masatake Haruta (Professor) have successfully combined gold nanoparticles with polyoxometalates (POMs), a promising support material which has already attracted considerable attention in catalysis, medicine, surface and material sciences.
POMs and their salts, molecular ion species of metallic oxides, are yet to see widespread use for the stabilization of gold particles. By mounting gold particles down to a size of 2 nm using a sol immobilization method, they successfully applied it to a low-temperature carbon monoxide (CO) gas purifier.
Their new gold-POM catalyst not only showed efficient conversion at -50°C, top class performance even for a gold nanoparticle catalyst, but also demonstrated stable, 100% removal of a 1%vol concentration of CO over a span of 35 days at 0°C, with no degradation of the material.
They found that smaller particle sizes led to better performance, and that the conversion efficiency of the material showed a unique dependence on temperature. This led to the discovery that trace amounts of water were essential to the function of the material, the first unique mechanism proposed for catalysis in gold/POM catalysts.
The technique and newly discovered mechanism not only promise a greater understanding of catalysis, but also potential application to industrial filtration, both for gases and liquids.
###
This study was supported by the “Nanotechnology Platform” Program of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan. The manuscript reporting this finding has been published online in Angewandte Chemie, International Edition.












