
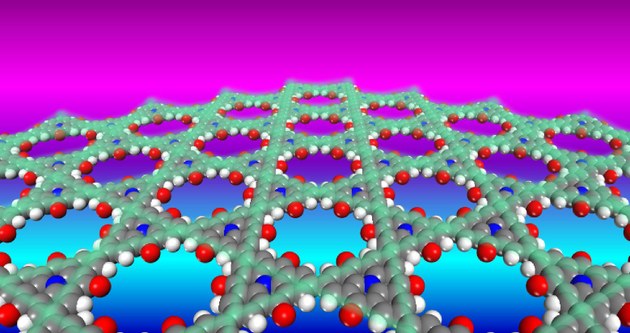
Honeycomb-kagome structure
© Yu Jing
Ultrathin materials are extremely interesting as building blocks for next generation nano electronic devices, as it is much easier to make circuits and other complex structures by shaping 2D layers into the desired forms.
Thomas Heine, Professor for Theoretical Chemistry at TU Dresden, is working on the prediction of such innovative materials. Their properties can be precisely calculated using modern methods of computational chemistry, even before they have been realized in the laboratory.
This research is particularly interesting for 2D polymers: their lattice type is defined by the shape of their building blocks, and those can be selected from the almost infinite variety of plane organic molecules which match the required structure.
A particularly interesting example is the kagome lattice, which consists of the corners and edges of a trihexagonal tiling. In 2019, Yu Jing and Thomas Heine proposed to synthesize such 2D polymers from triangular organic molecules (so-called triangulenes). These materials have a combined honeycomb-kagome structure (see figure).
Their calculations suggest that these 2D structures combine the properties of graphene (quasi massless charge carriers) with those of superconductors (flat electronic bands).
Now the Italian materials scientist Giorgio Contini and his international team have succeeded in synthesizing this 2D honeycomb kagome polymer, as published in Nature Materials earlier this week. An innovative surface synthesis method made it possible to produce crystals of such high quality that they were suitable for the experimental characterization of electronic properties.
Indeed, the predicted fascinating topological properties were revealed. Thus, for the first time, it could be experimentally proven that topological materials can be realized via 2D polymers.
Research on 2D polymers is thus placed on a solid basis. The kagome lattice described here is only one example out of hundreds of possibilities to connect plane molecules to regular lattices. For some of these variants, other interesting electronic properties have already been predicted theoretically. This opens up numerous new possibilities for theorists and experimentalists in chemistry and physics to develop materials with previously unknown properties.
Prof. Heine explains: “These results show that 2D polymers can be materials with useful electronic properties, although their structures are much more wide-meshed than regular electronic materials, with distances of more than one nanometer between the lattice points. The prerequisite is that the materials are of excellent structural quality.
This includes a high crystallinity and a very low defect density. Another important contribution of the colleagues around Prof. Contini is that, although the 2D polymers were produced on a metal surface, they can be detached and transferred to any other substrate, such as silicon oxide or mica, and thus be incorporated into electronic devices”.
Thomas Heine
Professor of Theoretical Chemistry
TU Dresden
Email: thomas.heine@tu-dresden.de
Yu Jing and Thomas Heine. “Making 2D Topological Polymers a reality” Nature Materials. URL: https://rdcu.be/b4fgL












