
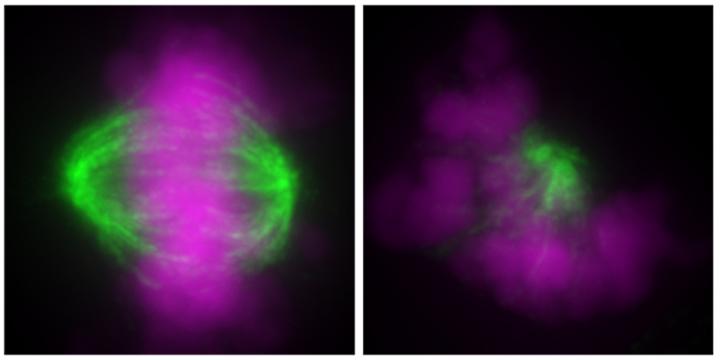
A diploid cell (left) and a haploid cell (right) showing normal and abnormal orientation of chromosomes (purple) and microtubules (green) during cell division, respectively.
Credit: Yaguchi K., et al., Journal of Cell Biology, April 30, 2018
Usage Restrictions: This image is copyrighted and can be used for reporting this press release if properly credited.
In mammals, including humans, cells which make up the body are diploids, which means that a cell contains a pair of each chromosome. A non-diploid state destabilizes the properties of the cells, triggering abnormalities, cancers and other serious diseases.
In asexual reproduction and cancer development, haploid (one set of each chromosome) and tetraploid (four sets of each chromosome) cells are generated, causing chromosomes to become unstable. However, why this instability occurs when the cell is in a non-diploid state has remained unknown.
In the present study, the researchers used human cell lines with different ploidy states — haploid, diploid and tetraploid — to investigate the effect of the differences on the cell replication process.
In normal cells, there are two centrosomes, which are regulators of cell replication. The researchers observed gradual loss of centrosomes in haploid cells and frequent over-duplication of centrosomes in tetraploid cells, both of which triggered frequent abnormalities in the cell replication process.
In addition, researchers found that there were fewer cellular fibers, called microtubules, in haploid cells, and more in tetraploid cells.
This was significant, as the number of these fibers was found to be a key factor that changes the efficiency of centrosome duplication, resulting in either centrosome loss or over-duplication.
On the other hand, the efficiency of DNA replication, which is another important step in cell replication, remained constant, regardless of a cell's ploidy.
“Incompatibility between centrosome duplication and the DNA replication cycle could be the underlying cause of the instability in non-diploid cells in mammals,” says Ryota Uehara. “Our findings could help understand chromosome instability in cancer cells, which are often in a non-diploid state, and lead to new cancer treatment strategies.”















