
Cornell marine biologist’s persistence leads to discovery of invasive sea squirts in vital Maine fishing grounds
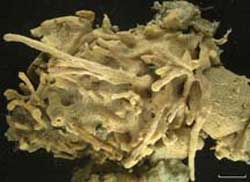
Thanks to the doggedness of a Cornell University marine biologist, researchers have discovered that one of Maine’s most important fishing areas has been invaded by an alien tunicate, or sea squirt, that could threaten the commercial fishing industry there.
A rapid assessment survey for marine invasive species in Cobscook Bay in August found a type of sea squirt — Didemnum sp. — that can damage ocean floor habitats and commercial species that live there. The survey was conceived and organized by Robin Hadlock Seeley, a visiting fellow in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at Cornell.
The invading sea squirt, first documented on the eastern coast of the United States in the 1970s and believed to be the byproduct of importing Japanese oysters for aquaculture, spreads rapidly by forming mats that look like blobs of pancake batter. It already has overrun some 40 square miles of Georges Bank, a prime offshore fishing area about 160 miles from outer Cape Cod.
“When a 2003 Rapid Assessment funded by the Environmental Protection Agency limited its search for invasive species in Maine to Casco Bay in southern Maine, I became very concerned that important bays farther north, such as Cobscook Bay, weren’t included in this survey,” said Seeley, whose long-term research has focused on predator-prey interactions in the Cobscook Bay ecosystem.
So she went to The Nature Conservancy about two years ago looking for support, wrote grants to fund a survey of Cobscook Bay within the state of Maine, invited investigators to participate and then coordinated the logistics for some 20 marine biologists to investigate the bay for three days in early August by taking samples from docks, buoys, boat ramps and fish farms.
“We now know that the Didemnum is definitely present in these waters,” said Seeley, who noted that the bay is an important source of scallops, mussels, lobsters and clams and is home to salmon and sea urchin aquaculture operations. “We do not yet know, however, to what extent Didemnum has spread throughout the bay. Further research and monitoring is needed.”
She noted that the waters of Cobscook Bay, which are near the Canadian border, may be too cold for Didemnum to spread and to pose a major threat to the area at present but that rising sea surface temperatures could allow the squirt to spread in the future.
Her survey not only discovered a potentially threatening species in eastern Maine, but also demonstrated that a locally funded survey could be effective without reliance on federal agencies to fund expensive, large-scale regional projects. In addition to Maine’s chapter of The Nature Conservancy, the survey was supported by Maine Sea Grant, the Cobscook Bay Resource Center, the Maine State Planning Office and the Maine Department of Marine Resources.
“Now that we’ve shown that a local approach to funding and supporting a rapid assessment survey is possible, other coastal communities may want to follow suit to survey their waters to determine if any invasive species are present and whether they pose an ecological or economic threat,” said Seeley, who also serves as the associate curator of Cornell’s malacology (mollusks, such as chitons, clams, mussels, snails, sea slugs, octopus and squid) collection.
Other researchers who participated in the three-day survey with Seeley included those from the University of Maine, University of New Hampshire — including Larry Harris who found theDidemnum as part of the survey — the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Williams College-Mystic Seaport Maritime Studies Program, the Royal Ontario Museum in Canada and University of Washington.














