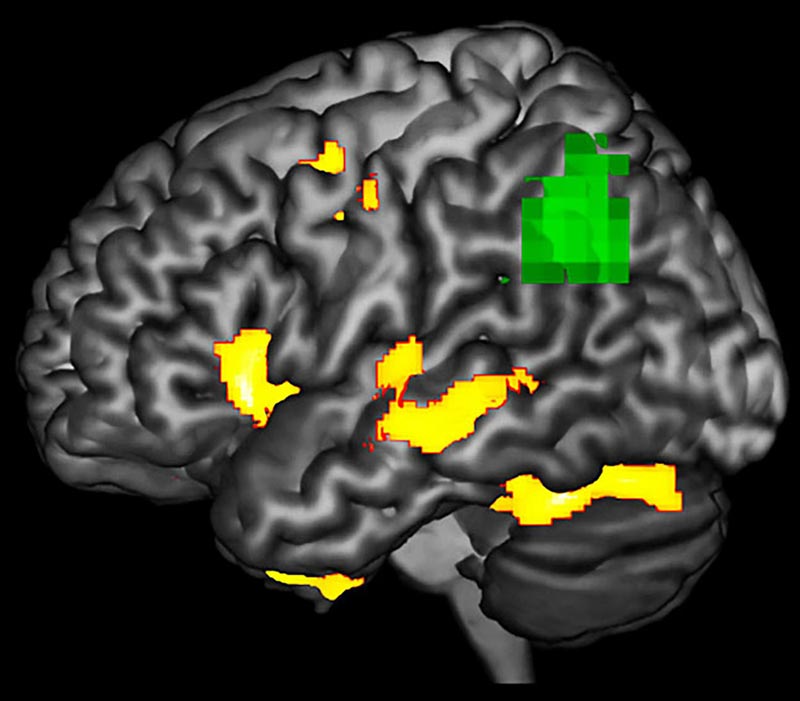
This image highlights areas in a PPA-affected brain during a language task where researchers observe functional abnormality (green) and structural degenerating (yellow). The green areas may be at-risk or dysfunctional, even if the neurons are not dead yet.
Courtesy: Aneta Kielar
Usage Restrictions: This visual may only be used in conjunction with reporting on or posting of this news release. Credit must be given as indicated.
Scientists might have found an early detection method for some forms of dementia, according to new research by the University of Arizona and the University of Toronto's Baycrest Health Sciences Centre.
According to the study published in the journal Neuropsychologia last month, patients with a rare neurodegenerative brain disorder called Primary Progressive Aphasia, or PPA, show abnormalities in brain function in areas that look structurally normal on an MRI scan.
“We wanted to study how degeneration affects function of the brain,” said Aneta Kielar, the study's lead author and assistant professor in the UA Department of Speech, Language and Hearing Sciences.
But what she and her team discovered was that the brain showed functional defects in regions that were not yet showing structural damage on MRI.
Structural MRI provides 3D visualization of brain structure, which is useful when studying patients with diseases that literally cause brain cells to wither away, like PPA.
Magnetoencephalography, or MEG, on the other hand, “gives you really good spatial precision as to where the brain response originates. We want to know if the decreased brain function is coming from the areas that are already atrophied or areas in an earlier stage of decline,” said Jed Meltzer, the study's senior author and an assistant professor of psychology at the University of Toronto.
Kielar and her colleagues compared brain scans of patients with PPA to healthy controls while both groups performed language tasks. The researchers also imaged participants' brains while at rest. The functional defects were related to worse performance in the tasks, as individuals with PPA lose their ability to speak or understand language while other aspects of cognition are typically preserved.
Identifying the discrepancy between a PPA brain's structural and functional integrity could be used as an early-detection method.
This is promising because “many drugs designed to treat dementia are proving to be not really affective and that might be because we're detecting the brain damage too late,” Kielar said. “Often, people don't come in for help until their neurons are already dead. We can do compensation therapies to delay disease progress, but once brain cells are dead, we can't get them back.” This technique could allow patients to get ahead of the damage.
Kielar acknowledged that this was a small study, which is partially because PPA is such a rare form of dementia, and that further investigation is needed.
Next, she hopes to uncover why this structural and functional mismatch is happening in PPA brains.
“It's interesting that the affected areas are so far from the neurodegeneration,” Kielar said. “One reason this might be happening is that those areas could be connected with white matter tracts,” which facilitate communication between different brain regions. “When one area is dead, the area connected to it doesn't get normal input. It doesn't know what to do, so it starts to lose its function and atrophy because it doesn't get stimulation.”
###
This study was supported by the Ontario Brain Institute Ontario Neurodegenerative Disease Research Initiative, an Alzheimer's Association New Investigator Research Grant (NIRG-12-236224) and a postdoctoral research award from the Ontario Research Coalition (ORC).












