New microscopy technology augments surgeon's view for greater accuracy
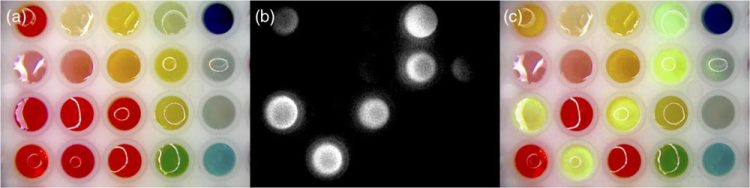
These are custom colored dye solutions with randomly plated ICG solution: (a) visible view through microscope, (b) NIR view seen on computer monitor, and (c) augmented view seen in real time through the ocular of the augmented microscope. Credit: © the authors, Journal of Biomedical Optics doi:10.1117/1.JBO.20.10.106002
Researchers at the University of Arizona (UA) have developed a prototype of a new microscope technology that could help surgeons work with a greater degree of accuracy. The new technology, call augmented microscopy, overlays images depicting diagnostic information such as blood flow and cancerous tissue over real images of blood vessels and other tissues and structures being viewed in the microscope.
A report on the work by Jeffrey Watson and co-authors from the UA departments of Biomedical Engineering and Surgery was published today in the Journal of Biomedical Optics, published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics.
Surgical microscopes are highly specialized stereomicroscopes installed on articulated mounts and provide a long working distance and functional enhancements, and are widely used in certain delicate operations, notably neurosurgery.
Within the last decade, surgical microscopes have been combined with near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging, in which contrast agents are injected into tissue and their fluorescence detected in NIR scans. The scans may reveal patterns of blood flow, or differentiate cancerous from normal tissue.
But there are limitations. For example, some microscopes used in complex vascular surgeries switch between two different views: the fully optical bright-field (real) view and the computer-processed projection of NIR fluorescence. The NIR image is two-dimensional, and on its own lacks the spatial cues that would help the surgeon identify anatomical points of reference. So the surgeon must visualize how the fluorescence in the NIR image lines up with the respective anatomical structures shown in the bright-field view.
The UA researchers' article, “Augmented microscopy: Real-time overlay of bright-field and near-infrared fluorescence images” describes their prototype of an augmented stereomicroscope that presents a simultaneous view of real objects in the surgical field and computer-processed images superimposed in real time.
“Surgeons want to see the molecular signals with their eyes, so that they can feel confident about what is there,” said journal associate editor Brian Pogue of Dartmouth College. “Too often, what they see is a report of the signals depicted in false color on a monitor. By displaying information through the surgical scope itself, the surgeon then sees the information with his or her own eyes.”
Pogue said he sees the work being important in advancing the translation of research into clinical practice. “There are very few papers on this idea of augmenting the surgical field of view that the surgeon sees, yet this is a high-interest topic,” he said. “This article presents a very practical idea and innovative implementation which is well done technically.”
The prototype offers advantages over earlier versions of augmented microscopes. By utilizing the optical path of the stereomicroscope, it maintains full three-dimensional stereoscopic vision, which is lost in fully digital display systems.
It also retains the imaging environment familiar to surgeons, including key features of surgical microscopes such as real-time magnification and focus adjustments, camera mounting, and multiuser access.
One possible application for this augmented microscope is laser surgery. In the past, surgeons could not see the laser beam through the standard stereomicroscope, nor anatomical details in the NIR images.
The researchers also suggest that this technology will be useful in the surgical treatment of brain tumors. Surgeons aggressively removing a tumor run the risk of damaging normal brain tissue and impairing the patient's brain functions; on the other hand, incomplete removal of a tumor results in immediate relapse in 90% of patients. Being able to simultaneously see the surgical field and the contrast agent identifying cancerous tissue within the augmented microscope may allow surgeons to remove these challenging tumors more accurately.
###
The work was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health.
Lihong Wang, Gene K. Beare Distinguished Professor of Biomedical Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, is editor-in-chief of the Journal of Biomedical Optics. The journal is published in print and digitally in the SPIE Digital Library, which contains more than 430,000 articles from SPIE journals, proceedings, and books, with approximately 18,000 new research papers added each year.
About SPIE
SPIE is the international society for optics and photonics, an educational not-for-profit organization founded in 1955 to advance light-based science and technology. The Society serves nearly 264,000 constituents from approximately 166 countries, offering conferences and their published proceedings, continuing education, books, journals, and the SPIE Digital Library in support of interdisciplinary information exchange, professional networking, and patent precedent. SPIE provided more than $4 million in support of education and outreach programs in 2014. SPIE is a Founding Partner of the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies and a Founding Sponsor of the U.S. National Photonics Initiative. http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



