PET Scans Identify Prostate Cancer Patients for Targeted Radiation
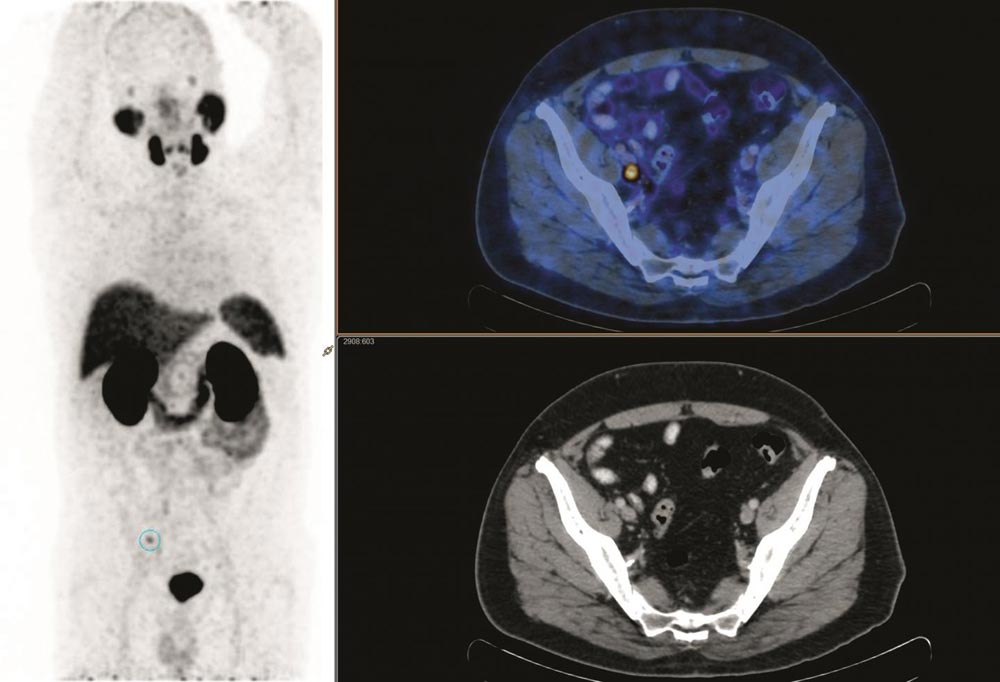
A 69-year-old man presented with rising PSA (0.16ng/ml) following radical prostatectomy for Gleason score 7 prostate cancer 4 years prior. PSMA PET CT showed a solitary pelvic node with no prostate fossa recurrence. The patient underwent salvage radiotherapy including both fossa and pelvic node fields. PSA continued to rise, and repeat PSMA imaging showed new sites of PSMA-avid nodal disease in the common iliac region, directly above the radiotherapy field.
Credit: L Emmett et al., St Vincent's Hospitals, Sydney, Australia
For prostate cancer patients who have rising levels of PSA (a cancer indicator) even after radical prostatectomy, early treatment makes a difference. In a study featured in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, Australian researchers demonstrate that PET scans can identify which of these prostate cancer patients would benefit from salvage radiation treatment (SRT).
“The research is novel because it looks at the impact of PSMA PET/CT on patient responses to treatment, not just on whether the PET scan results in changed management,” explains Louise Emmett, MD, of the St. Vincent's Hospital, Sydney, Australia. She elaborates, “In the study, these patients underwent imaging with a PSMA PET scan and had treatment based on the results of the scan findings. The study then followed how these men were treated, and whether the treatment was effective.”
Results of the study, which ultimately included 146 men of whom 99 received SRT, show an overall treatment response after SRT of 72 percent. Among patients with a negative PSMA, 44 percent (27 of 60) underwent SRT, while 56 percent (33 of 60) did not. The negative PSMA group that received SRT had an 85 percent treatment response (23 of 27), while 65 percent (22 of 34) of the negative PSMA patients not receiving SRT experienced increases in prostate-specific antigen (PSA). For those with disease confined to the prostate fossa (36 of 99), 83 percent (29 of 36) responded to SRT. For men with nodal disease (26 of 99), 61 percent (16 of 26) had treatment response following SRT.
The study demonstrates that PSMA PET can independently predict treatment response to SRT. Men with negative or fossa-confined PSMA have the highest treatment response to SRT, while men with cancerous nodes or distant disease have a poor response. In particular, a negative PSMA PET predicts a high response to SRT.
Emmett points out, “The results of the study show that PSMA PET is more predictive of a treatment response than PSA level, surgical margins or seminal vesical involvement.”
She notes, “In addition, men with a negative PSMA PET scan were the most likely to respond to salvage radiotherapy with a significant treatment response. However, men with a negative PSMA PET were also the least likely to receive radiotherapy treatment. The majority of men with a negative PSMA PET scan who did not receive treatment had a significant rise in their PSA levels, some to levels at which they were no longer curable. While further study of larger patient groups with longer follow-up times is needed for this cohort of prostate cancer patients, this study is pivotal in providing evidence for change in practice.”
###
Authors of “Treatment outcomes from 68Ga PSMA PET-CT-informed salvage radiation treatment in men with rising PSA following radical prostatectomy: Prognostic value of a negative PSMA PET” include Louise Emmett, Garvan Institute of Medical Research/The Kinghorn Cancer Centre, St. Vincent's Hospital, and University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia; Pim J. van Leeuwen and Matthijs J. Scheltema, Australian Prostate Cancer Research Centre, New South Wales, Australia; Rohan Nandurkar, University of New South Wales; Thomas Cusick, Phillip Stricker and Quoc Nguyen, Australian Prostate Cancer Research Centre and Garvan Institute of Medical Research/The Kinghorn Cancer Centre; George Hruby, Andrew Kneebone and Thomas Eade, Royal North Shore Hospital and Genesis Cancer Care, Sydney, Australia; Gerald Fogarty and Raj Jagavkar, Genesis Cancer Care; Bao Ho, St. Vincent's Public Hospital; and Anthony M. Joshua, Garvan Institute of Medical Research/The Kinghorn Cancer Centre.
Please visit the SNMMI Media Center to view the PDF of the study, including images, and more information about molecular imaging and personalized medicine. To schedule an interview with the researchers, please contact Laurie Callahan at (703) 652-6773 or lcallahan@snmmi.org. Current and past issues of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine can be found online at http://jnm.
About the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) is an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to raising awareness about nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, vital elements of precision medicine that allow diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes.
SNMMI's more than 15,000 members set the standard for molecular imaging and nuclear medicine practice by creating guidelines, sharing information through journals and meetings and leading advocacy on key issues that affect molecular imaging and therapy research and practice. For more information, visit http://www.












