
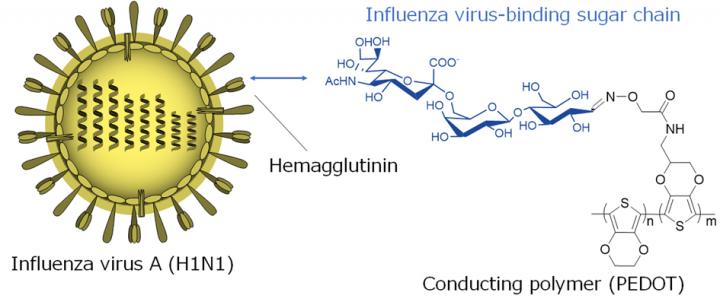
A new conducting polymer was developed for detecting specific interaction of trisaccharide with hemagglutinin in the envelope of the human influenza A virus (H1N1) by electrical manners.
Credit: Department of Bioelectronics,Institute of Biomaterials and Bioengineering,TMDU
Conventional tests for detecting the flu virus are often slow and expensive, and can miss early viral infections. In contrast, the new biosensor measures tiny changes in voltage in an electrically conductive polymer to quickly detect virus concentrations almost 100 times smaller than the limit of currently available kits. The work was done at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), in a collaboration between the Institute of Biomaterials and Bioengineering and the Department of Molecular Virology.
Conductive polymers are a class of carbon-based molecules that conduct electricity, but can also be used in biological environments. They are very attractive materials for biosensor applications because researchers can easily attach biomolecules to the polymers, which allow them to bind with specific targets, such as flu viruses. In this study, poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) was modified with a functional group that binds with the H1N1 human influenza virus, but not avian flu strains.
“Conducting polymers have several advantages over inorganic counterparts,” explains corresponding author Yuji Miyahara. “These include the ability to conduct both electrical and ionic carriers, mechanical flexibility, low cytotoxicity, low-cost production by casting or printing, and tunable properties via chemical synthesis or doping.”
To construct the biosensor, the polymer film was placed between two electrodes. When a solution containing H1N1, which carries a tiny positive charge on its exterior shell, was added, some of the viruses stuck to the polymer and increased the voltage measured by the electrodes. This electrical method allows the sensor to detect the presence of miniscule amounts of the virus.
Viral loads are often measured in hemagglutination units (HAU). The new sensor can detect viral concentrations as small as 0.013 HAU. By comparison, commercially available kits that use immunochromatographic tests only work for concentrations greater than about 1.13 HAU. This represents an almost 100-fold increase in sensitivity.
Study coauthor Shoji Yamaoka stressed the clinical applications of the device. “We developed a conducting polymer-based sensor that can recognize a specific virus, which makes it a good candidate for wearable monitoring and point-of-care testing.”
The article, “Specific Recognition of Human Influenza Virus with PEDOT Bearing Sialic Acid-Terminated Trisaccharides” was published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces at DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b02523












