
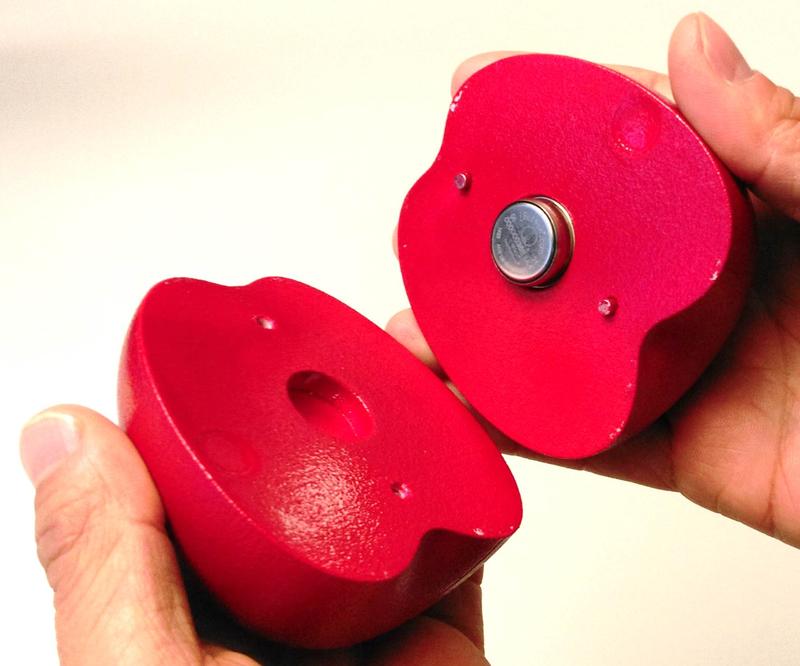
Empa's artificial fruit sensor – here in the Braeburn version.
Empa
Mangos, bananas and oranges have usually travelled long distances by the time they reach our shops. They are picked, packaged, refrigerated, packed in refrigerated containers, shipped, stored and finally laid out on display. However, not all the cargo makes it safely to its destination. Although fruit is inspected regularly, some of it is damaged or may even perish during the journey.
This is because monitoring still has significant scope for improvement. Although sensors measure the air temperature in the freight container, it is the core temperature of the individual fruit that is decisive for the quality of the fruit. However up to now, it has only been possible to measure this “invasively”, i.e. by inserting a sensor through the skin and into the centre.
And even this process has drawbacks. To carry out the measurement, the technician usually takes a piece of fruit from a cardboard box in the front row of pallets in the container, which in turn distorts the result. Fruit that is closer to the outside of the transport container is better refrigerated than fruit on the inside.
Sometimes whole container loads have to be destroyed because the temperatures on the inside of the container did not meet the prescribed guidelines. The USA and China, in particular, are extremely strict regarding the importation of fruit and vegetables. If the cargo has not been stored for three weeks at a certain minimum temperature, it is not authorised for sale in the country.
Not only does refrigeration serve to maintain the freshness and quality of the fruit, it also kills any larvae, such as moth larvae, which can nest in the fruit. It is therefore essential to prove that the refrigeration has actually penetrated all the fruit in the whole consignment for the required period of time.
The sensor travels with the fruit
In order to guarantee and monitor the temperature within the fruit, researchers at Empa have now developed an artificial fruit sensor. It is the same shape and size as the relevant fruit and also simulates its composition, and can be packed in with the real fruit and travel with it. On arrival at the destination, the data from the sensor can be analysed relatively quickly and easily. From this, the researchers hope to gain information about the temperature during transportation.
This is important information, primarily for insurance reasons: if a delivery does not meet the quality requirements, the sensor can be used to establish the point in the storage and transport chain at which something went wrong. Initial results are certainly very promising: “We analysed the sensors in the Empa refrigeration chamber in detail and all the tests were successful,” explains Project Manager Thijs Defraeye from the Laboratory for Multiscale Studies in Building Physics. Field tests are currently under way at Agroscope in Wädenswil.
An artificial fruit sensor for Braeburn and Jonagold apples
However, the same sensor does not work for all fruits, as Defraeye explains. “We are developing separate sensors for each type of fruit, and even for different varieties.” There are currently separate sensors for the Braeburn and Jonagold apple varieties, the Kent mango, oranges and the classic Cavendish banana. In order to simulate the characteristics of the individual types of fruit, the fruit is X-rayed, and a computer algorithm creates the average shape and texture of the fruit. From the literature or based on their own measurements, the researchers then determine the exact composition of the fruit's flesh (usually a combination of water, air and sugar) and simulate this in exactly the same ratio in the laboratory, although not with the original ingredients, instead using a mixture of water, carbohydrates and polystyrene.
This mixture is used to fill the fruit-shaped sensor mould. The mould is produced on a 3D printer. The researchers place the actual sensor inside the artificial fruit, where it records the data, including the core temperature of the fruit. Existing measuring devices on container walls only provide the air temperature, but this is not sufficiently reliable because the fruit can still be too warm on the inside. Although such fruit core simulators already exist in the field of research, they are not yet sufficiently accurate, explains Defraeye. One such example that has been used is balls filled with water with a sensor inside. “We have conducted comparative tests,” says the researcher. “And our filling provided much more accurate data and simulated the behaviour of a real piece of fruit much more reliably at different temperatures.”
Not (yet) wireless
Initial field tests on the sensors are currently under way and the researchers are now looking for potential industrial partners to manufacture the fruit spies. The investment is certainly likely to be worthwhile. It is estimated that the cost of such a sensor is less than CHF 50. The data would only have to be analysed if something was wrong with the delivered goods. This would then make it possible to efficiently establish where in the process an error had occurred.
Another desirable feature would be to be able to receive the data from the cargo container live and in real time, so that appropriate countermeasures could be taken in the event of abnormal data – thereby potentially saving the fruit cargo. That would require a wireless or Bluetooth connection. “However, our current fruit sensor cannot do that yet. And the price of the product would, of course, go up,” says Defraeye. But the profits for the companies would probably also go up if the fruit sensors enabled them to supply more goods in perfect condition.
http://www.empa.ch/web/s604/fruit-sensor












