
PRECISE-DAPT Score
Department of Cardiology, Inselspital, Bern University Hospital
Spending less time in hospital, having to take less medication after surgery – both are concerns shared by most patients. In a study published this month, the Department of Cardiology of Inselspital addressed this concern.
In accordance with the principle of weighing benefits and risks, upon which all medical treatments are based, it took an in-depth look at medicinal after-care from the patients’ perspective.
After surgery on the coronary arteries, patients routinely receive platelet-inhibiting drugs for approx. one year. This is intended to prevent heart attacks. These drugs, however, may cause bleeding complications in some patients. Until now, doctors have been unable to find out how high the risk of bleeding was for each person.
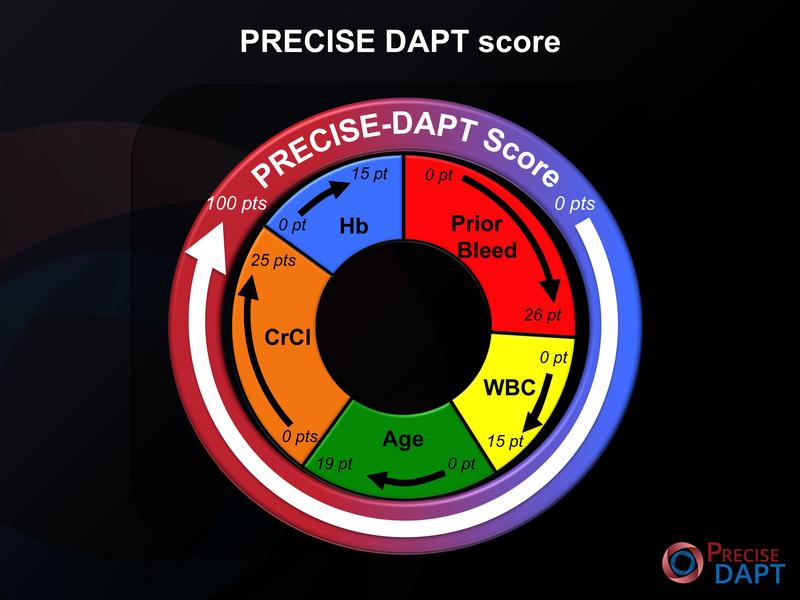
Personalised after-care thanks to a simple test
In a multicentric study under the direction of Prof. Marco Valgimigli, from the Department of Cardiology of Inselspital, cardiologists have now developed a simple five-part test: This identifies the individual bleeding risk based on the factors of age, kidney function, haemoglobin level, number of white platelets and previous spontaneous bleedings.
In the case of a high risk, the drugs are prescribed for only approx. three months – because this period of time the patient benefits from the protective effect against heart attack, but has no serious side-effects.
People without an increased risk of bleeding, on the other hand, can take the medicinal coronary prophylaxis for longer because, with good protection, they do not have to worry about bleedings.
Contact:
Prof. Dr. med. Marco Valgimigli, Senior Physician, Department of Cardiology, Inselspital, Bern University Hospital, +41 31 632 47 14, marco.valgimigli@insel.ch.
http://thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(17)30397-5/fulltext
http://www.precisedaptscore.com












