
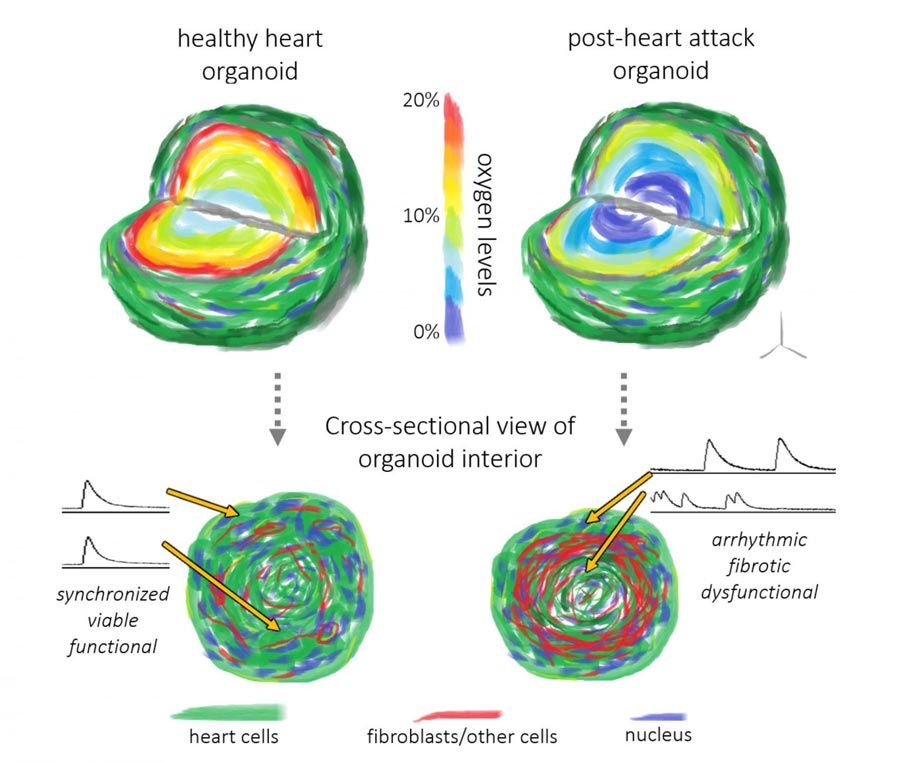
Low-oxygen cell culture conditions combined with human heart organoids recreate tissue-level features of a post-heart attack heart.
Image courtesy of lead author Dr. Dylan Richards, graduate of the MUSC Clemson Bioengineering Program
In the U.S., someone has a heart attack every 40 seconds, and yet researchers have not had a model that fully mimics what occurs in the human heart after a heart attack.
A team of investigators at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) and Clemson University recently reported in an article in Nature Biomedical Engineering that they have developed human cardiac organoids less than 1 millimeter in diameter that closely resemble the physiological conditions that occur during a heart attack.
The team was led by bioengineer Ying Mei, Ph.D., who holds a joint faculty position at MUSC and Clemson University. He is part of the MUSC Clemson Bioengineering program, which places Clemson bioengineers and bioengineering doctoral students on the MUSC campus so that they can interact with clinicians in need of engineering solutions. The article's lead author, Dylan Richards, Ph.D., is a graduate of the joint program.
“We were essentially able to take that 3D complex nature of a heart attack and then downsize it into a microtissue model,” said Richards.
Organoids are three-dimensional multicellular tissues that are less than 1 millimeter in diameter. These organoids, or microtissues, function like their full-size counterparts. In this case, the heart organoids actually beat and contract as the human heart does. This model uses induced pluripotent stem cells, almost like “parent cells,” that divide and mature into several types of heart cells that interact and self-assemble to form the organoid.
Traditionally, biologists use cells in a dish or animal models, such as mice or rats, to model diseases being studied. These methods have their own disadvantages that the organoid model overcomes.
Cells in a dish are great for learning things at the cellular level, but it is very unnatural for cells to grow in two dimensions on a flat surface.
Animal models are very useful in taking the next steps toward recapitulating what happens in the human body, but organoids, especially those for the heart, are the closest to recreating what occurs in humans.
“The hearts of rats and mice beat five to 10 times faster than those of humans,” Richards explained. “How those mechanisms work physically -the electrophysiology and the pumping action – is just different because of the scale.”
In contrast, the cardiac organoid recreates a human version of the heart and closely resembles the tissue dysfunction that takes place after the oxygen shortage caused by a heart attack. Because it is very difficult to obtain a sample immediately after a heart attack occurs, most of what we know about heart attacks comes from observations made long after the initial oxygen shortage. The organoid model fills in this gap, enabling visualization immediately after oxygen deprivation.
“This can help us to understand better how cells respond in the short term and, in turn, how that makes way for long-term damage,” said Richards of the organoid model.
This model also enables researchers to test whether heart drugs improve heart attack outcomes.
“It could help us determine whether a drug is effective at preventing some of this damage or preventing a detrimental response to an oxygen shortage,” explained Richards.
The model could also provide a way to test whether a drug that is safe in a healthy heart is also safe in a diseased one. Such information could guide physicians in prescribing drugs more appropriately in patients who had preexisting heart conditions at the time of the heart attack.
In short, the model provides researchers with an understanding of the early events of a heart attack that they have not had before. But Mei intends to make the model even better by including immune cells. Immune cells are responsible for cleaning out any dead cells caused by the heart attack, but by doing so, they can determine how immune cells play a role in the restructuring of heart tissue after damage from an oxygen shortage. The Mei lab would like to study how they do so in hopes of preventing the death of damaged but still living areas of the heart.
Mei would also like to examine the effects of patients' genetics on their outcomes. His laboratory is currently working on creating organoids from cells from patients with diverse outcomes. Those organoids can then be used to help us to understand more fully how a patient's specific genetic profile affects his or her recovery.
“We are not the first ones to recapitulate the cellular or even the tissue-level response. I would argue, however, that we are the first ones to recapitulate the organ-level response,” said Mei.
Special note: Mei, Richards and their co-authors would like to dedicate this work to their dear friend and co-author Craig Beeson, Ph.D., who was lost to cancer before the publication of their article.
###
About the Medical University of South Carolina
Founded in 1824 in Charleston, MUSC is the oldest medical school in the South as well as the state's only integrated academic health sciences center with a unique charge to serve the state through education, research and patient care. Each year, MUSC educates and trains more than 3,000 students and 800 residents in six colleges: Dental Medicine, Graduate Studies, Health Professions, Medicine, Nursing and Pharmacy. The state's leader in obtaining biomedical research funds, in fiscal year 2019, MUSC set a new high, bringing in more than $284 million. For information on academic programs, visit http://musc.
As the clinical health system of the Medical University of South Carolina, MUSC Health is dedicated to delivering the highest quality patient care available while training generations of competent, compassionate health care providers to serve the people of South Carolina and beyond. Comprising some 1,600 beds, more than 100 outreach sites, the MUSC College of Medicine, the physicians' practice plan and nearly 275 telehealth locations, MUSC Health owns and operates eight hospitals situated in Charleston, Chester, Florence, Lancaster and Marion counties. In 2019, for the fifth consecutive year, U.S. News & World Report named MUSC Health the No. 1 hospital in South Carolina. To learn more about clinical patient services, visit http://muschealth.
MUSC and its affiliates have collective annual budgets of $3.2 billion. The more than 17,000 MUSC team members include world-class faculty, physicians, specialty providers and scientists who deliver groundbreaking education, research, technology and patient care.












