Infection defense: call for support by the killer cells
Killer cells – called cytotoxic T cells in the technical jargon – are somewhat like a well-trained police dog: as long as they don’t know that an infection is currently spreading somewhere in the body, they behave peacefully. They only become active and multiply when forensics rubs a “piece of property” of the pathogen under their nose. Only then do they head out to destroy the intruder.
The role of forensics is assumed by the dendritic cells. They patrol around the clock and keep a lookout for molecules that should not actually be inside the body. When they make a find, they present the foreign molecule on their surface. Then they wait for a killer cell, to which they can show their find.
However, there are a great many different killer cells in the body. Each of them specializes in a certain foreign substance and can only be activated by a specific one. It thus usually takes a little time until the right bloodhound comes across the dendritic cell. But then things happen quickly: the killer cell begins to divide rapidly. Within a couple of days, an army of special forces is thus created, which can advance towards the pathogen.
Cooperation at a cellular level
“We have investigated what has to happen so that the killer cells multiply as effectively as possible,” explains Prof. Wolfgang Kastenmüller. The scientists at the Institute of Experimental Immunology at the University of Bonn led a study involving researchers from Japan, the USA, Italy and Germany. “Until now, it was thought that contact with the dendritic cell was sufficient here. However, we were able to show that the killer cell first forms a kind of team by ordering up other cell types in a targeted way.
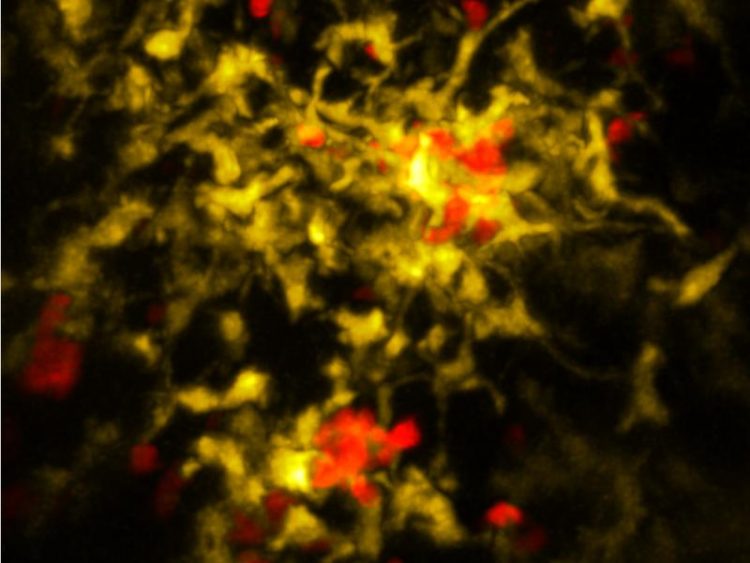
Immediately after instruction by a dendritic cell, the killer cell thus triggers a kind of chemical help signal. Images from a special microscope show for the first time how specialized cells of the body’s defenses then head towards it. Upon arrival, these helpers set various immune processes in motion. Only in this way is the killer cell fully activated.
This now begins to divide significantly. What’s more, the arising army differentiates itself: some cells become particularly strong, but short-lived, killers. Others, meanwhile, become a kind of memory cell, which can be activated quickly in the event of another infection.
“The killer cell thus first creates a very specific microenvironment,” emphasizes Kastenmüller. “This is essential for a coordinated and strong immune defense mechanism.” The scientists hope that their fundamental work will open up new possibilities over the long term for further improving vaccinations against viruses or tumors.
Publication: A. Brewitz et al.: CD8+ T cells orchestrate pDC – XCR1+ dendritic cell spatial and functional cooperativity to optimize priming; Immunity; DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.01.003
Contact:
Prof. Wolfgang Kastenmüller
Institute of Experimental Immunology
University of Bonn
Tel. +49 (0)228/28711040
E-mail: wkastenm@uni-bonn.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-bonn.deAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



