
Xiaohu Xia
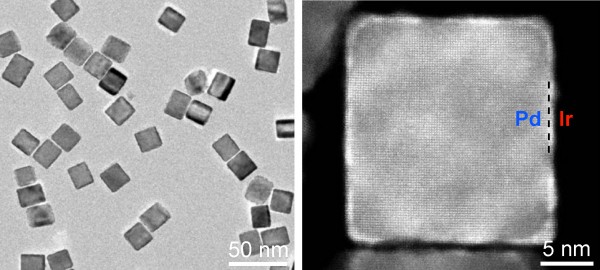
A research team led by Michigan Tech chemist Xiaohu Xia developed a catalyst that improves the sensitivity of the standard PSA test over 100-fold. The catalyst, pictured above, is made of palladium nanocubes coated with iridium.
Say you’ve been diagnosed with prostate cancer, the second-leading cause of cancer death in men. You opt for surgery to remove your prostate. Three months later, a prostate surface antigen (PSA) test shows no prostate cells in your body. Everyone rejoices.
Until 18 months later, when another PSA test reveals that now prostate cells have reappeared. What happened?
The first PSA test yielded what’s known as a false negative result. It did not detect the handful of cells that remained after surgery and later multiplied. Now a chemist at Michigan Technological University has made a discovery that could, among other things, slash the numbers of false negatives in PSA tests.
Xiaohu Xia and his team, including researchers from Louisiana State University and the University of Texas–Dallas, have developed a new catalyst that could make lab tests like the PSA much more sensitive. And it may even speed up reactions that neutralize toxic industrial chemicals before they enter lakes and streams.
Their new catalyst mimics the action of similar biochemicals found in nature, called peroxidases. “In animals and plants, these peroxidases are important— for example, they get rid of hydrogen peroxide, which is harmful to the organism,” said Xia. In medicine, peroxidases have become powerful tools for accelerating chemical reactions in diagnostic tests; a peroxidase found in the horseradish root is commonly used in the standard PSA test.
However, these natural peroxidases have drawbacks. They can be difficult to extract and purify. “And, they are made of protein, which isn’t very stable,” Xia explained. “At high temperatures, they cook, like meat.”
“Moreover, their efficiency is just fair,” he added. “We wanted to develop a mimic peroxidase that was substantially more efficient than the natural peroxidase, which would lead to a more-sensitive PSA test.”
Contact Information
Xiaohu Xia, assistant professor of chemistry
Michigan Technological University
xiaxh@mtu.edu
(906) 487-2048















