
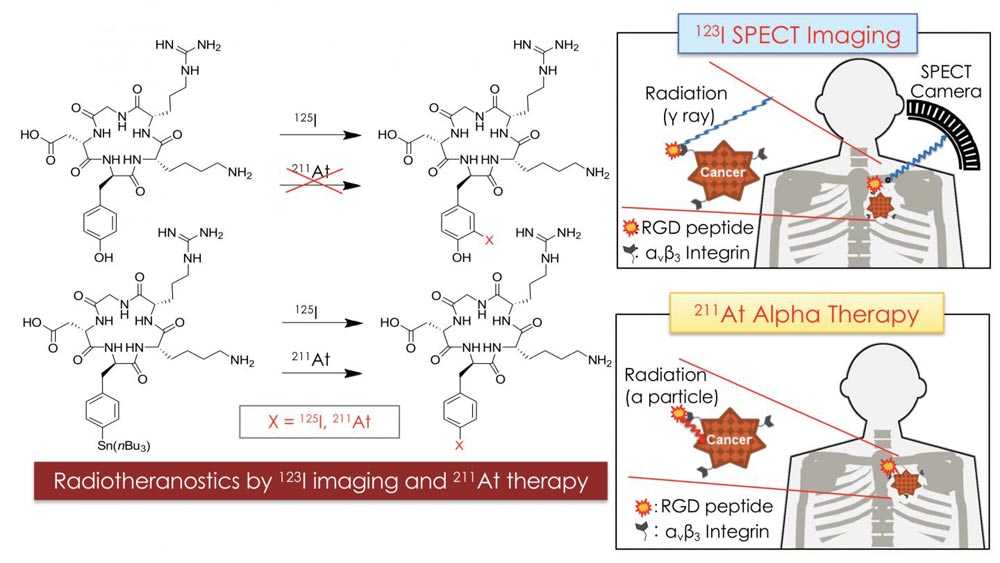
The concept radiotheranostics using At-211 and I-123 for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Combination of SPECT imaging using I-123-labeled RGD peptide with targeted alpha therapy using At-211-labeled RGD peptide could be useful for personalized medicine to cancer.
Credit: Kanazawa University
In recent years, an approach combining therapy and diagnosis both based on radioisotopes, called 'radiotheranostics', has gained significance. The key idea is that both the diagnostic and the therapeutic isotope can be brought to a tumor by attaching it to the same carrier molecule.
Now, Kazuma Ogawa from Kanazawa University and colleagues have synthesized a radiotheranostic system with astatine (At-211) as the alpha-particle emitter and iodine (I-123) as the gamma-radiation source.
A few types of molecules can be used as radioisotope carriers. Ogawa and colleagues were able to use a peptide (a biomolecule consisting of a chain of amino acids) as the carrier for both the astatine and the iodine isotope.
Specifically, they worked with a peptide containing the so-called RGD sequence of amino acids. The RGD motif plays an important role in cell membrane binding; its cell-adhesive activity makes it a good component for designing molecules for targeting tumors.
The theranostic carrier molecules were synthesized through a series of chemical reactions, the last step being a halogenation — the replacement of a particular molecular component by a halogen. (Both astatine and iodine are halogens, having similar chemical properties.)
After the successful synthesis of the At-211 and I-125 carrier molecules, the researchers tested their behavior in vivo. They simultaneously injected the two compounds in tumor-bearing mice, and looked at the biodistribution of the radioactive isotopes — that is, in which parts of the body they occur, and how abundantly.
The main finding was that the At-211- and I-125-labeled RGD peptides displayed biodistributions that were very similar, with a high accumulation in the tumor — a prerequisite for operating as a theranostic system. (Another iodine isotope, I-123, is foreseen to be the diagnostic radioisotope, but I-125 has a much longer half-life, making it easier to work with in the present experiments.)
The work of Ogawa and colleagues is an important step forward in the development of radiotheranostics. Quoting the scientists: “This method could be applicable to other peptides directly targeted to cancer. Moreover, future efforts should be focused on application of other radiohalogens … as positron emitters for PET [positron-electron tomography] imaging … “












