
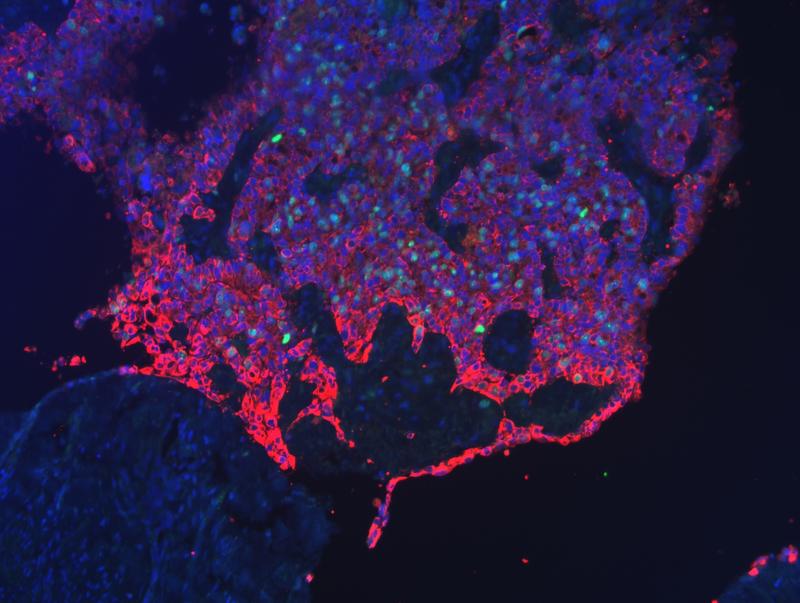
Fluorescence image of a tumour front of the cervix. Cell nuclei are shown in blue and dividing cells in green. Tumour cells, marked in red, infiltrate and suppress healthy tissue.
Photo: Leipzig University Hospital
“Our approach equips surgeons with a roadmap for the surgical removal of tumours, giving patients a much better chance of survival, reducing the likelihood of relapse and minimising operative morbidity,” explains Hans Kubitschke of Leipzig University’s Peter Debye Institute for Soft Matter Physics, who co-authored the publication together with Benjamin Wolf of the UKL’s Department of Gynaecology. They both drew up the so-called roadmap together with other physicists from the University and medical professionals from UKL.
In their research, the scientists use pathological data from over 500 cases and computer simulations of tumour spread to show that the growth potential of cervical cancer is not the same in all directions and that the probability of spread varies greatly between different anatomical structures in the immediate vicinity of the uterine cervix.
Some anatomical structures, for example the tissue of the urinary bladder, were affected significantly more frequently than others, such as the ureter and the rectum. “There is a connection between the probability of infiltration and the ontogeny of tissues – so-called compartments:
compartments exhibiting a lesser ontogenetic distance to the uterine cervix are more likely to be infiltrated by the tumour than tissues of greater ontogenetic distance,” explains Wolf. According to the researchers, tissue mapping can be used to predict the probability of tumour spread in a specific tissue.
The findings provide a basis for understanding and predicting the local spread of cervical cancer, with the ontogenetic characterisation of tissue probably able to serve as a “risk map” to local cancer growth.
“Knowing the embryological origin of any tissue in which cancer arises, one can derive a relative likelihood of different adjacent tissues to be infiltrated by tumour cells,” explains physicist Professor Josef Alfons Käs.
In theory, surgical removal of tumours could therefore be tailored precisely to the endangered tissue. In future, this knowledge could help reduce mortality rates in patients undergoing tumour surgery by sparing low-risk tissue while improving local tumour control.
Original title of the publication in Scientific Reports:
“Roadmap to Local Tumour Growth: Insights from Cervical Cancer”, doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49182-1
Hans Kubitschke
Tel: +49341-97 32481
Email: hans.kubitschke@uni-leipzig.de
http://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-49182-1












