
Advancements in Carbon Nanotube Optics for Quantum Cryptography
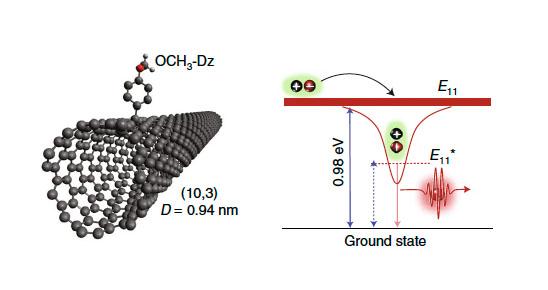
Depiction of a carbon nanotube defect site generated by functionalization of a nanotube with a simple organic molecule. Altering the electronic structure at the defect enables room-temperature single photon emission at telecom wavelengths.
Credit: LANL
“We are particularly interested in advances in nanotube integration into photonic cavities for manipulating and optimizing light-emission properties,” said Stephen Doorn, one of the authors, and a scientist with the Los Alamos National Laboratory site of the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies (CINT).
“In addition, nanotubes integrated into electroluminescent devices can provide greater control over timing of light emission and they can be feasibly integrated into photonic structures. We are highlighting the development and photophysical probing of carbon nanotube defect states as routes to room-temperature single photon emitters at telecom wavelengths.”
The team's overview was produced in collaboration with colleagues in Paris (Christophe Voisin) who are advancing the integration of nanotubes into photonic cavities for modifying their emission rates, and at Karlsruhe (Ralph Krupke) where they are integrating nanotube-based electroluminescent devices with photonic waveguide structures. The Los Alamos focus is the analysis of nanotube defects for pushing quantum emission to room temperature and telecom wavelengths, he said.
As the paper notes, “With the advent of high-speed information networks, light has become the main worldwide information carrier. . . . Single-photon sources are a key building block for a variety of technologies, in secure quantum communications metrology or quantum computing schemes.”
The use of single-walled carbon nanotubes in this area has been a focus for the Los Alamos CINT team, where they developed the ability to chemically modify the nanotube structure to create deliberate defects, localizing excitons and controlling their release.
Next steps, Doorn notes, involve integration of the nanotubes into photonic resonators, to provide increased source brightness and to generate indistinguishable photons. “We need to create single photons that are indistinguishable from one another, and that relies on our ability to functionalize tubes that are well-suited for device integration and to minimize environmental interactions with the defect sites,” he said.
“In addition to defining the state of the art, we wanted to highlight where the challenges are for future progress and lay out some of what may be the most promising future directions for moving forward in this area. Ultimately, we hope to draw more researchers into this field,” Doorn said.
###
Publication: Carbon nanotubes as emerging quantum-light sources, Nature Materials, DOI 10.1038/s41563-018-0109-2
Funding: Los Alamos National Laboratory Directed Research and Development funding, and support from the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, a U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science user facility.
Related news items: “Single-photon emitter has promise for quantum info-processing”
http://www.
About Los Alamos National Laboratory (http://www.
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, a team composed of Bechtel National, the University of California, BWX Technologies, Inc. and URS Corporation for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health and global security concerns.












