
European XFEL Launches Second X-Ray Light Source for Research
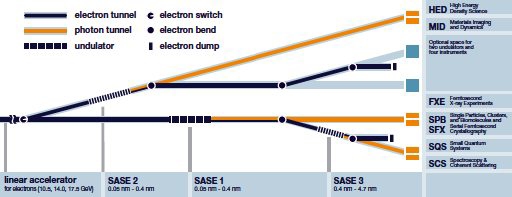
Beamlines of the European XFEL
The European XFEL will provide light sources (beamlines) for X-ray flashes with different properties.
Copyright: European XFEL
SASE3 will serve two experiment stations scheduled to begin user operation at the end of the year. Since the start of operation in September 2017, 340 scientists from across the globe have already used the facility for their research. The successful start of operation of the new SASE 3 source will enable the facility to increase the number of users further.
European XFEL Managing Director Prof. Robert Feidenhans’l said: “The construction and commissioning of the new light source are complex processes, for which we and our DESY colleagues have been preparing intensely for these last weeks and months. We are very happy that the commissioning of this second light source SASE 3 has also run so smoothly, and that both sources, SASE1 and SASE3, produce light simultaneously.
For this I would like to thank all those involved, in particular the accelerator team from DESY. We continue to be on schedule to start operation at all four experiment stations currently under construction, beginning with the first two instruments in November. The remaining two will start operation at the beginning of 2019. This will increase our current capacity threefold by mid 2019.”
The new X-ray light source SASE3 uses electrons that have first passed through the light source SASE1 where they have already produced laser light. SASE3 provides laser light that will provide X-ray light for the experiment stations SQS and SCS, which are currently under construction.
The SQS instrument (Small Quantum Systems) is specialized for the study of fundamental processes such as how chemical bonds break in molecules, or what happens on the atomic level when materials absorb many photons at the same time.
The SCS instrument (Spectroscopy and Coherent Scattering) will focus on the investigation of fast changes in material properties, such as within magnetic materials, materials that withstand extreme temperatures, superconducting materials, and also biological samples. The research at these two stations has relevance for basic research but also for the development of new materials in the fields of IT, medicine, energy research, and catalysts, among others.
Dr. Winni Decking, responsible for the operation of the European XFEL accelerator at DESY, explained: “The first X-ray laser light at SASE3 is a special moment for the technicians, engineers, and scientists who, over many years, have contributed to the construction of the facility with great care and precision. The fact that we have achieved this milestone so soon after the first round of user operation also shows how well the operation teams from DESY and European XFEL work together.”
The European XFEL X-ray laser light is extremely intense and million times brighter than current synchrotron light sources. With the European XFEL, up to 27 000 light flashes per second can be produced, making the facility unique worldwide. In order to accomplish this, the superconducting accelerator technology developed at DESY is used at European XFEL. The X-ray light flashes are produced in the tunnels from bunches of electrons that have been accelerated to nearly the speed of light and have a lot of energy. These bunches are repeated regularly at extremely short time intervals. Up to 200m long magnetic structures, so-called undulator systems, send the accelerated electrons on a tight slalom course. At every turn, the electron bunches send out X-ray light pulses that build on one another.
SASE3 is one of currently three undulator systems at European XFEL. SASE1 produced the first-ever X-ray light at European XFEL in May 2017. Now SASE3 follows on schedule. The first lasing from SASE2 is planned for the middle of 2018. SASE1 and SASE2 are 200 m long, very similar in their construction and produce extremely short-wavelength X-ray light. SASE3, which sits behind SASE1, is, at 120 m, somewhat shorter and produces longer-wavelength X-ray light.
The wavelengths attainable with SASE1 and SASE2 correspond to roughly the size of an atom. This, therefore, enables the capturing of pictures and films of the nano-cosmos in atomic resolution, such as of biomolecules that are important for the development of disease or for novel medication.
At the first lasing, SASE3 produced X-ray light with a wavelength of 1.4 nanometre (900 eV), about 600 times shorter than that of visible light. The start-up of operation began with 20 pulses per second; later this will increase to 27 000.
As a world first, the accelerated electrons are first used to produce laser light in SASE1 and then used in SASE3 to produce X-ray light a few hundred meters further downstream. The light sources, therefore, produce X-rays for different instruments in the experiment hall at the end of the tunnel at the same time. The planned simultaneous operation of several light sources and the experiment stations is a further unique characteristic of European XFEL and of particular importance due to the high international demand for experiment time.
Press contact: Dr. Bernd Ebeling, +49 (0)40 8998 6921, bernd.ebeling@xfel.eu
Information and Images: www.xfel.eu
About European XFEL
The European XFEL in the Hamburg area is a new international research facility of superlatives: 27,000 X-ray flashes per second and a brilliance that is a billion times higher than that of the best conventional X-ray sources open up completely new opportunities for science. Research groups from around the world will be able to map the atomic details of viruses, decipher the molecular composition of cells, take three-dimensional “photos” of the nanoworld, “film” chemical reactions, and study processes such as those occurring deep inside planets. The construction and operation of the facility is entrusted to European XFEL, a non-profit company that cooperates closely with its main shareholder, the research centre DESY, and other organisations worldwide. The company, which has a workforce of more than 300 employees, started user operation of the facility in September 2017. With construction and commissioning costs of 1.22 billion euro (at 2005 price levels) and a total length of 3.4 kilometres, the European XFEL is one of the largest and most ambitious European new research facilities to date. At present, 11 countries have signed the European XFEL convention: Denmark, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Poland, Russia, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland. The United Kingdom is in the process of joining.
http://media.xfel.eu/XFELmediabank/?l=en&c=12587 Pictures
http://www.xfel.eu European XFEL homepage












