
Ultrafast Coherent Magnetism: Light-Driven Material Innovation
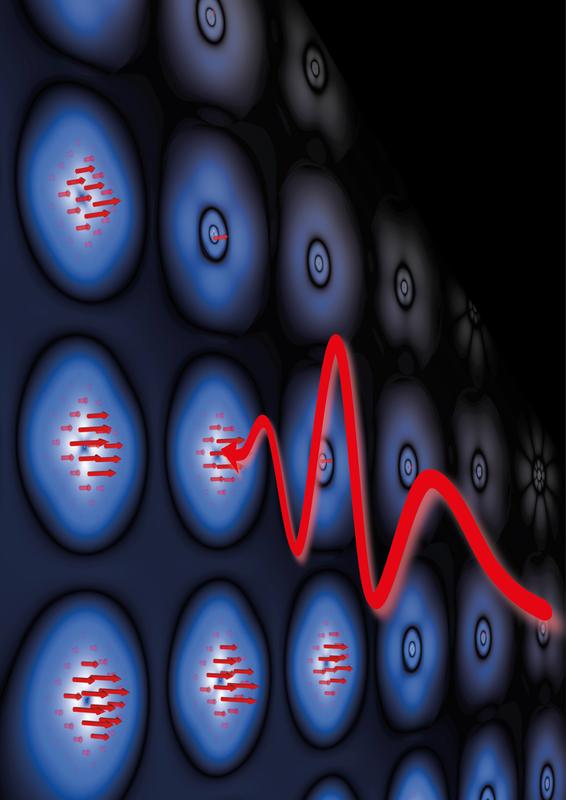
Recording of the fast switching of magnetic moments by ultrafast light pulses
© J.K. Dewhurst
Electronic properties of materials can be directly influenced via light absorption in under a femtosecond (10-15 seconds), which is regarded as the limit of the maximum achievable speed of electronic circuits.
In contrast, the magnetic moment of matter has only been able to be influenced up to now by a light and magnetism-linked process and roundabout way by means of magnetic fields, which is why magnetic switching takes that much longer and at least several hundred femtoseconds.
A consortium of researchers from the Max Planck Institutes for Quantum Optics and for Microstructure Physics, of the Max Born Institute, at the University of Greifswald and Graz University of Technology have only now been able to manipulate the magnetic properties of a ferromagnetic material on a time scale of electrical field oscillations of visible light – and thus in sync with the electrical properties – by means of laser pulses.
This influence was able to be accelerated by a factor of 200 and was measured and represented using time-resolved attosecond spectroscopy. The researchers described their experiment in the journal Nature.
Composition of the material as a crucial criterion
In attosecond spectroscopy, magnetic materials are bombarded with ultra-short laser pulses and electronically influenced. “The light flashes set off an intrinsic and usually delaying process in the material. The electronic excitation is translated into a change in magnetic properties,” explains Martin Schultze, who until recently worked at the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics in Munich, but who is now professor at the Institute of Experimental Physics at TU Graz. Due to the combination of a ferromagnet with a non-magnetic metal, the magnetic reaction in the described experiment, however, is brought about as fast as the electronic one.
“By means of the special constellation, we were optically able to bring about a spatial redistribution of the charge carrier, which resulted in a directly linked change in the magnetic properties,” says Markus Münzenberg. Together with his team in Greifswald, he developed and produced the special material systems.
Schultze is enthusiastic about the scale of the success of the research: “Never before has such a fast magnetic phenomenon been observed. Through this, ultrafast magnetism will take on a completely new meaning.”
Sangeeta Sharma, researcher at the Max Born Institute in Berlin who predicted the underlying process using computer models, is impressed: “We are expecting a significant development boost from this for all applications in which magnetism and electron spin play a role.”
Initial step towards coherent magnetism
Furthermore, the researchers show in their measurements that the observed process runs coherently: this means the quantum mechanical wave nature of the moving charge carriers is preserved. These conditions allow scientists to use individual atoms as information carriers instead of larger units of material or to influence the changing magnetic properties using another specifically delayed laser pulse, thus advancing technological miniaturisation.
“Regarding new perspectives, this could lead to similar fantastic developments as in the field of magnetism, such as electronic coherence in quantum computing,” says Schultze hopefully, who now leads a working group focusing on attosecond physics at the Institute of Experimental Physics.
Development of top research at TU Graz
Together with his colleagues from Graz, Schultze wants to expand the institute into a centre for ultrafast time-resolved spectroscopy of electronic and magnetic phenomena. To this end, a modern laser laboratory is being built at TU Graz’s Campus Neue Technik, which – based on existing activities – will continue to enhance research in the FoE Advanced Materials Science at TU Graz.
The research of Martin Schultze is anchored in the Field of Expertise “Advanced Materials Science”, one of five research foci of TU Graz.
Univ.-Prof. Martin SCHULTZE
TU Graz | Institute of Experimental Physics
Petersgasse 16, 8010 Graz, Österreich
Tel. +43 316 873 8142
schultze@tugraz.at
Dr. Sangeeta SHARMA
Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy
Max-Born Strasse 2A, 12489 Berlin, Germany
Tel.: +49 30 6392 1321
sharma@mbi-berlin.de
Univ.-Prof. Markus MÜNZENBERG
University of Greifswald | Institute of Physics
Felix-Hausdorff-Str. 6, 17489 Greifswald, Germany
Tel.: +49 3834 420-4780
markus.muenzenberg@uni-greifswald.de
The paper'Light-wave dynamic control of magnetism' was published in Nature within the link https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1333-x
(DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1333-x)












