
'Growing' active sites on quantum dots for robust H2 photogeneration
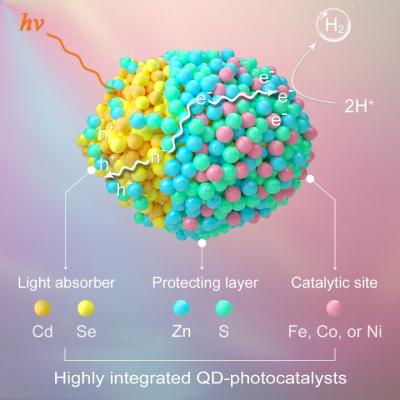
Schematic diagram of site- and spatial- selective integration of metal ions into QDs for robust H2 photogeneration
Credit: Prof. WU's Group
This research, published online in Matter, was conducted by a research team led by Prof. WU Lizhu and Dr. LI Xubing from the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry (TIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Photosynthesis in nature provides a paradigm for the large-scale conversion of sunlight into chemical fuels.
For example, hydrogenases in certain bacteria and algae catalyze the reversible reduction of protons to H2 with remarkable activity.
Inspired by natural photosynthesis, solar-driven H2 evolution from water is regarded as an ideal pathway to store solar energy in chemical bonds.
In pursuing of highly efficient chemical transformation, QDs in conjunction with non-noble metal ions have appeared as the cutting-edge technology of H2 photogeneration.
This research successfully realized the cooperative and well-controlled loading of non-noble metal ions in QDs, thereby integrating light absorber, protecting layer and active site together in an ultra-small nanocrystal, which would show great potentials in fabricating artificial photosynthetic devices for scale-up solar-to-fuel conversion.
Time-resolved spectroscopic techniques and density functional theory calculations reveal the kinetics of interfacial charge transfer and the mechanism of H2 evolution at active species, which provides new guidance on the design of multifunctional photocatalysts for practical applications.
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the National Science Foundation of China, and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Science.















