
Rocket Science Innovations Transform Kidney Dialysis Techniques
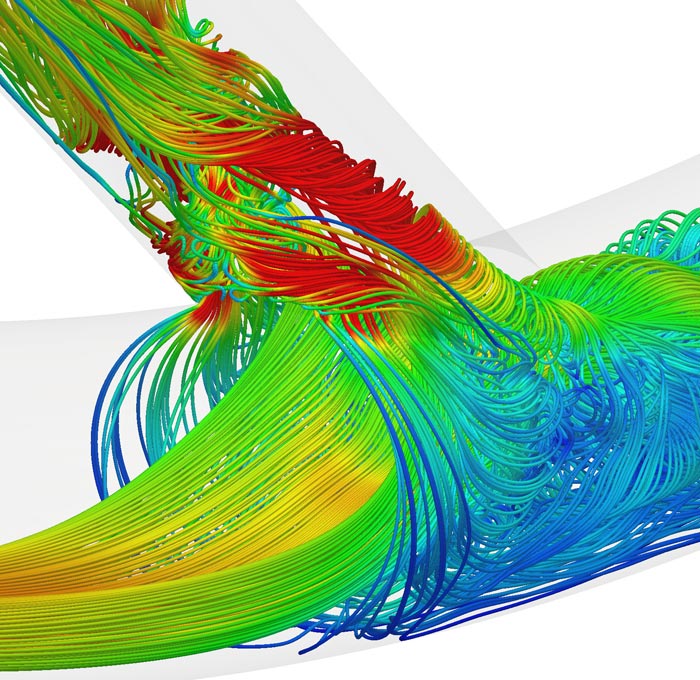
Peter Vincent/Imperial College London
Streamlines of flow within an idealized Arterio-Venous Fistulae. The color of the lines corresponds to the speed of the blood—red being highest, and blue lowest.
A team of researchers in the United Kingdom has found a way to redesign an artificial connection between an artery and vein, known as an Arterio-Venous Fistulae, which surgeons form in the arms of people with end-stage renal disease so that those patients can receive routine dialysis, filtering their blood and keeping them alive after their kidneys fail.
The new design, described in the journal Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, may decrease the likelihood of blockages in Arterio-Venous Fistulae, which is a major complication of dialysis.
While the AVF would have to prove effective in clinical trials before they could be deemed a success, the researchers are enthusiastic about their approach, which used software from the aerospace industry to design the novel configurations.
“At the moment, the process of creating an Arterio-Venous Fistulae for dialysis is rather 'one-size-fits-all',” said Peter Vincent, a senior lecturer and EPSRC early career fellow in the Department of Aeronautics at Imperial College London. “Our ultimate aim is to use computational simulation tools to design tailored, patient-specific Arterio-Venous Fistulae configurations that won't block and fail.”
Dialysis and Chronic Kidney Disease
Dialysis is a life-saving treatment for end-stage renal disease — the last stage of chronic kidney disease — a serious and often fatal health condition in which a person's kidneys become damaged and can no longer filter blood as effectively as healthy kidneys. As a result, wastes from the blood remain within the body and often lead to other health problems such as cardiovascular disease, anemia and bone disease.
Chronic kidney disease is a global health challenge. For perspective, in the United States alone, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that more than 20 million adults — more than 10 percent of the U.S. adult population — may have the disease, although many are undiagnosed. Kidney disease is now the 9th leading cause of death in the U.S.
Once a person's kidney's fail, they require either a kidney transplant or regular treatment via a dialysis machine to keep filtering the blood like a kidney. Transplant surgeries often have very good outcomes, but the procedures are limited by the availability of donated kidneys, and only a few thousand become available every year in the United States, while tens of thousands of people are on the waiting list for a kidney transplant. People often wait for a new kidney transplant for years, having to undergo periodic dialysis the entire time.
One problem that arises with dialysis is that the connections made between the body and a dialysis machine via an Arterio-Venous Fistulae frequently become blocked and fail shortly after they are created — leading to unfavorable clinical outcomes and a significant additional cost burden for healthcare systems worldwide.
So an interdisciplinary team of U.K. researchers — including members from aeronautics, bioengineering, computational engineering, medical imaging and clinical medicine — from Imperial College London, Imperial College Renal and Transplant Centre at Hammersmith Hospital, and St. Mary's Hospital set out to design an Arterio-Venous Fistulae with reduced failure rates.
Design Based on Aerospace Software
To do this, the researchers first needed to gain a better understanding of how arterial curvature affects blood flow and oxygen transport patterns within Arterio-Venous Fistula.
Blood flow patterns within AVF are “inherently 'un-natural,' and it's thought that these unnatural flow patterns lead to their ultimate failure,” explained Vincent.
By using computational simulation software originally developed for the aerospace sector, the team is able to simulate and predict flow patterns in various Arterio-Venous Fistula configurations. “This allows us to design Arterio-Venous Fistula with much more natural flow patterns, which will hopefully reduce failure rates,” Vincent said.
The team “identified ways of constructing Arterio-Venous Fistula such that the flow is stabilized,” he added. “We discovered that if an Arterio-Venous Fistulae is formed via connection of a vein onto the outside of an arterial bend, it stabilizes the flow.”
The implications of this work are tremendous, because it may now finally be possible to design an Arterio-Venous Fistulae with reduced failure rates — offering improved clinical outcomes for patients with kidney failure who require dialysis.
The article, “The Effect of In-Plane Arterial Curvature on Blood Flow and Oxygen Transport in Arterio-Venous Fistulae,” is authored by F. Iori, L. Grechy, R.W. Corbett, W. Gedroyc, N. Duncan, C.G. Caro and P. Vincent. It appears in the journal Physics of Fluids on March 17, 2015 (DOI: 10.1063/1.4913754). After that date, it may be accessed at: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/pof2/27/3/10.1063/1.4913754
The authors of this paper are affiliated with Imperial College London, Imperial College Renal and Transplant Centre at Hammersmith Hospital and St. Mary's Hospital.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex or multiphase fluids. See: http://pof.aip.org
Contact Information
Jason Socrates Bardi, AIP
jbardi@aip.org
240-535-4954
@jasonbardi















