
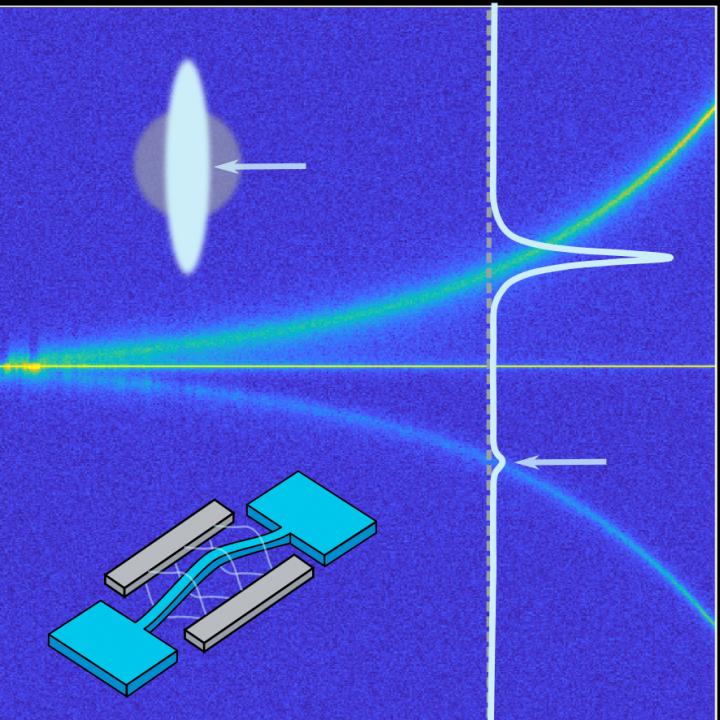
"Satellites" in the spectrum of a vibrating nanostring (lower image insert) for increasing drive power. The different brightnesses of the upper (green) and lower (blue) satellite encode the strength of the squeezing (upper image insert).
Credit: Weig Group, University of Konstanz
The research team led by physicist Professor Eva Weig at the University of Konstanz has now been able to show how such a squeezed state can be measured in a much simpler way than with the existing methods.
Moreover, the new method allows examining squeezed states in systems where such measurements were not possible before.
The results are published in the current issue of the journal Physical Review X.
###
Read the full article at campus.kn, the online magazine of the University of Konstanz: https:/
Key facts:
– Original publication: J. S. Huber, G. Rastelli, M. J. Seitner, J. Kölbl, W. Belzig, M. I. Dykman, and E. M. Weig. Spectral evidence of squeezing of a weakly damped driven nanomechanical mode. Physical Review X, 10, 021066, published on 23 June 2020
Link: https:/
– Development of a new method for measuring “squeezing”.
– Experiment by Jana Huber from the Nanomechanics Group of Professor Eva Weig at the University of Konstanz.
– Theoretical model by Professor Wolfgang Belzig and Dr Gianluca Rastelli from the University of Konstanz and Professor Mark Dykman from Michigan State University (USA).
– With financial support from the European FET Proactive Project HOT (732894), the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) as part of the QuantERA Project QuaSeRT (13N14777), and the Collaborative Research Centre SFB 767 “Controlled Nanosystems” at the University of Konstanz. Mark Dykman's research is funded by the National Science Foundation (Grant ? DMR-1806473). He is a Senior Fellow of the Zukunftskolleg at the University of Konstanz.
– campus.kn is the University of Konstanz's online magazine. We use multimedia approaches to provide insights into our research and science, study and teaching as well as life on campus.
Note to editors: Images can be downloaded here:
https:/
Caption: “Satellites” in the spectrum of a vibrating nanostring (lower image insert) for increasing drive power. The different brightnesses of the upper (green) and lower (blue) satellite encode the strength of the squeezing (upper image insert).
Image: Weig Group, University of Konstanz
https:/
Caption: Professor Eva Weig, Universität Konstanz
Image: University of Konstanz
Image: https:/
Caption: Jana Huber, University of Konstanz
Image: Rainer M. Hohnhaus















