
NASA's MAVEN spacecraft finds that 'stolen' electrons enable unusual aurora on Mars
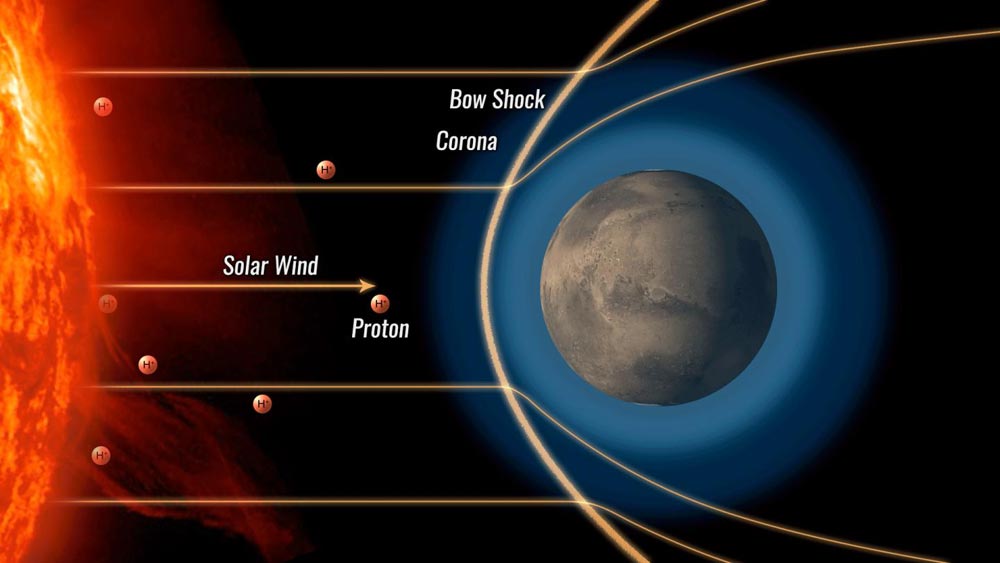
This animation shows a proton aurora at Mars. First, a solar wind proton approaches Mars at high speed and encounters a cloud of hydrogen surrounding the planet. The proton steals an electron from a Martian hydrogen atom, thereby becoming a neutral atom. The atom passes through the bowshock, a magnetic obstacle surrounding Mars, because neutral particles are not affected by magnetic fields. Finally, the hydrogen atom enters Mars' atmosphere and collides with gas molecules, causing the atom to emit ultraviolet light. Download animation: http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12986
Credit: NASA/MAVEN/Goddard Space Flight Center/Dan Gallagher
Auroras flare up when energetic particles plunge into a planet's atmosphere, bombarding gases and making them glow. While electrons generally cause this natural phenomenon, sometime protons can elicit the same response, although it's more rare.
Now, the MAVEN team has learned that protons were doing at Mars the same thing as electrons usually do at Earth–create aurora. This is especially true when the Sun ejects a particularly strong pulse of protons, which are hydrogen atoms stripped of their lone electrons by intense heat. The Sun ejects protons at speeds up to two million miles per hour (more than 3 million kilometers per hour) in an erratic flow called the solar wind.
The MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution mission) team was studying Mars' atmosphere with the Imaging UltraViolet Spectrograph (IUVS), and observed that on occasion, the ultraviolet light coming from hydrogen gas in Mars' upper atmosphere would mysteriously brighten for a few hours. They then noticed that the brightening events occurred when another MAVEN instrument, the Solar Wind Ion Analyzer (SWIA), measured enhanced solar wind protons.
But two puzzles make this type of aurora seem impossible at first glance: how did these protons get past the planet's “bow shock,” a magnetic obstacle which normally diverts the solar wind's charged particles around the planet? And how could the protons give off light, since atoms need electrons to do so?
“The answer was thievery,” said Justin Deighan, of the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado, Boulder, lead author of a paper on this research appearing July 23 in Nature Astronomy.
“As they approach Mars, the protons coming in with the solar wind transform into neutral atoms by stealing electrons from the outer edge of the huge cloud of hydrogen surrounding the planet. The bow shock can only divert charged particles, so these neutral atoms continue right on through.”
When those high-speed incoming atoms hit the atmosphere, some of their energy was emitted as ultraviolet light, which is invisible to the human eye but detectable to instruments like the IUVS on MAVEN. In fact, one incoming atom can collide with molecules in the atmosphere hundreds of times before it slows down, giving off a slew of ultraviolet photons.
“The Martian proton auroras are more than a light show,” said Jasper Halekas of the University of Iowa, responsible for the SWIA instrument. “They reveal that the solar wind is not completely diverted around Mars, by showing how solar wind protons can sneak past the bow shock and impact the atmosphere, depositing energy and even enhancing the hydrogen content there.”
Proton auroras do occur at Earth, but not as often as at Mars. One key difference is Earth's strong magnetic field, which diverts the solar wind away from Earth to a much greater degree than at Mars. On Earth, proton auroras only occur in very small regions near the poles, whereas at Mars they can happen everywhere.
However, proton auroras could be common on Venus and on Saturn's moon Titan. Like Mars, these two worlds lack their own magnetic fields, and have lots of hydrogen in their upper atmospheres–with plenty of electrons to share. Looking further, it's likely that many planets orbiting other stars have the same favorable conditions, and would be likely to have proton auroras too.
###
This research was funded by the MAVEN mission. MAVEN's principal investigator is based at the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, Boulder, and NASA Goddard manages the MAVEN project.












