
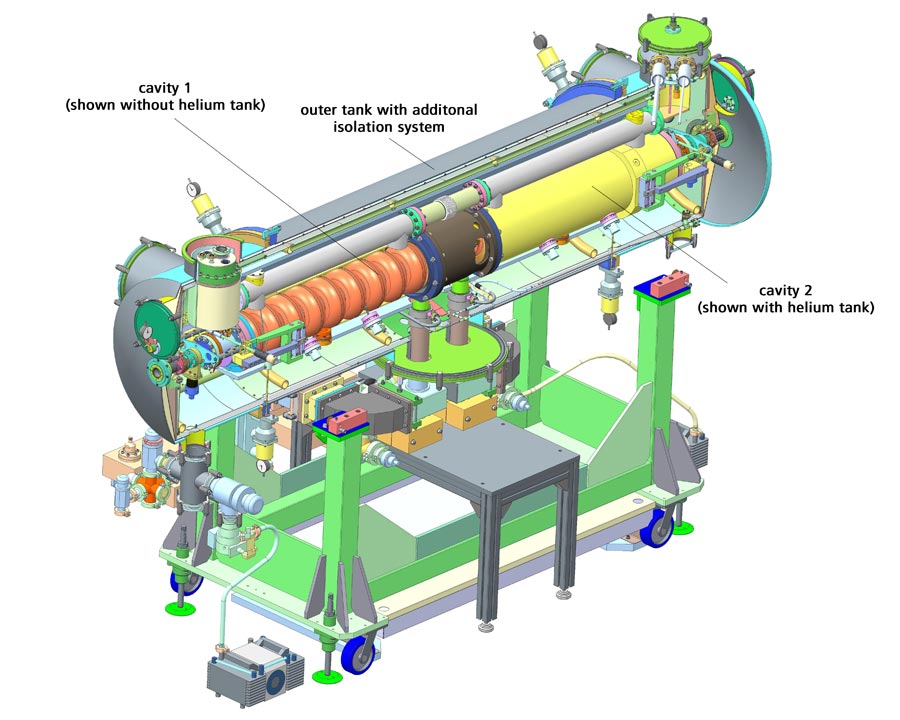
Cross-section through the highly complex accelerator module with its thermal-insulation system and the superconducting resonators (cavities).
© Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR)
As the production of two superconducting accelerator modules for the future electron accelerator MESA (“Mainz Energy-Recovering Superconducting Accelerator”) at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) gets on its way, the MESA project launches into its next phase.
MESA is based on a unique concept for recovering a part of the energy that is required for accelerating the electron beam. “The operating costs of MESA can thus be reduced significantly”, said Professor Kurt Aulenbacher, head of the project team. MESA is the central instrument for several key experiments at the Cluster of Excellence “Precision Physics, Fundamental Interactions and Structure of Matter” (PRISMA). These include precision measurements of the proton radius and the search for so-called dark photons, i.e., particles that may explain the mystery of dark matter.
At the end of May 2015, the entire project team for producing the superconducting accelerator modules met on site for the first time. The team, which includes engineers, physicists, and production specialists of both the Institute of Nuclear Physics at Mainz University and the manufacturing company Research Instruments, discussed technical details and fixed the production schedule for the modules, each of which will measure nearly four meters in length.
These modules are highly complex technical components of modern linear accelerators, which use electromagnetic alternating fields to bring elementary particles — in the case of MESA, electrons — close to the speed of light. The MESA modules are superconducting and therefore have to be kept at a temperature of minus 271.3 degrees Celsius, close to absolute zero. They consist of a system for thermal insulation, a so-called cryostat, with built-in superconducting resonators, so-called cavities. These cavities are made of niobium, a metal that turns superconducting at very low temperatures.
To ensure that the required operating temperature of minus 271.3 degrees Celsius is maintained, the cavities are welded into a tank that is flushed with liquid helium. The helium tank with the cavities inside is, in turn, enclosed in another tank, similar to a thermos. For additional isolation, liquid nitrogen is passed through a system of pipes arranged between helium and outer tank.
MESA will be the world's first superconducting energy-recovering accelerator dedicated to research. “With the high intensity and quality of its beam, MESA provides a unique platform for a forward-looking experimental program to study and test the limits of currently known phenomena in elementary particle physics. This is one of the core objectives of PRISMA,” said Professor Hartmut Wittig, spokesperson for the PRISMA Cluster of Excellence, from whose resources the development and construction of MESA is funded.
The researchers of Mainz University involved in PRISMA are eagerly awaiting the commissioning of MESA, which is planned for 2017, not least as the accelerator will have an instrumental role when it comes to securing a second round of funding for the Cluster of Excellence.
Further information:
Professor Dr. Kurt Aulenbacher
Institute of Nuclear Physics
Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
D 55099 Mainz, GERMANY
Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
phone +49 6131 39-25804
e-mail: aulenbac@mail.uni-mainz.de
http://www.kph.uni-mainz.de/eng/
Dr. Felix Schlander
Institute of Nuclear Physics
Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
D 55099 Mainz, GERMANY
phone: +49 6131 39-22954
e-mail: schland@uni-mainz.de
http://www.kph.uni-mainz.de/eng/
http://www.prisma.uni-mainz.de – PRISMA Cluster of Excellence at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz















