
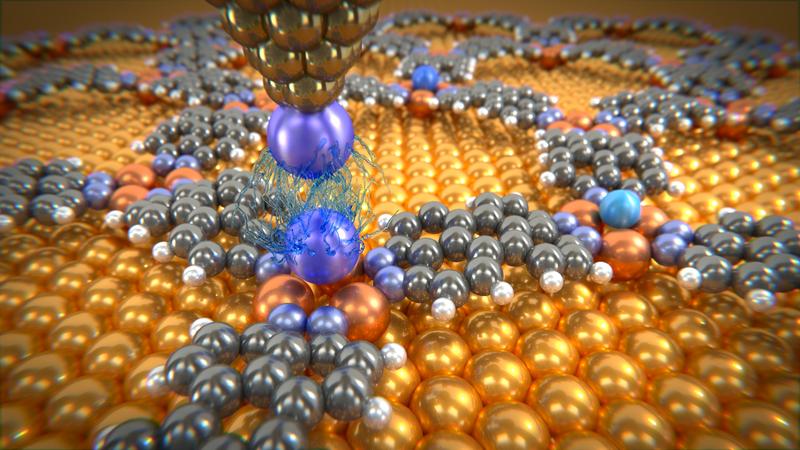
Rare gas atoms deposited on molecular network are investigated with a probing tip decorated with a xenon atom. The measurements give information about van der Waals forces between individual atoms.
University of Basel, Department of Physics
Van der Waals forces act between non-polar atoms and molecules. Although they are very weak in comparison to chemical bonds, they are hugely significant in nature. They play an important role in all processes relating to cohesion, adhesion, friction or condensation and are, for example, essential for a gecko’s climbing skills.
Van der Waals interactions arise due to a temporary redistribution of electrons in the atoms and molecules. This results in the occasional formation of dipoles, which in turn induce a redistribution of electrons in closely neighboring molecules. Due to the formation of dipoles, the two molecules experience a mutual attraction, which is referred to as a van der Waals interaction. This only exists temporarily but is repeatedly re-formed. The individual forces are the weakest binding forces that exist in nature, but they add up to reach magnitudes that we can perceive very clearly on the macroscopic scale – as in the example of the gecko.
Fixed within the nano-beaker
To measure the van der Waals forces, scientists in Basel used a low-temperature atomic force microscope with a single xenon atom on the tip. They then fixed the individual argon, krypton and xenon atoms in a molecular network. This network, which is self-organizing under certain experimental conditions, contains so-called nano-beakers of copper atoms in which the noble gas atoms are held in place like a bird egg. Only with this experimental set-up is it possible to measure the tiny forces between microscope tip and noble gas atom, as a pure metal surface would allow the noble gas atoms to slide around.
Compared with theory
The researchers compared the measured forces with calculated values and displayed them graphically. As expected from the theoretical calculations, the measured forces fell dramatically as the distance between the atoms increased. While there was good agreement between measured and calculated curve shapes for all of the noble gases analyzed, the absolute measured forces were larger than had been expected from calculations according to the standard model. Above all for xenon, the measured forces were larger than the calculated values by a factor of up to two.
The scientists are working on the assumption that, even in the noble gases, charge transfer occurs and therefore weak covalent bonds are occasionally formed, which would explain the higher values.
The international team of scientists from Switzerland, Japan, Finland, Sweden and Germany used the experimental set-up above to measure the smallest forces ever detected between individual atoms. In doing so, the researchers have demonstrated that they can still push ahead into new fields using atomic force microscopy, which was developed exactly 30 years ago.
Original source
Shigeki Kawai, Adam S. Foster, Torbjörn Björkman, Sylwia Nowakowska, Jonas Björk, Filippo Federici Canova, Lutz H. Gade, Thomas A. Jung, and Ernst Meyer
Van der Waals interactions and the limits of isolated atom models at interfaces
Nature Communications (2016), doi: 10.1038/ncomms11559
Further information
Prof. Dr. Ernst Meyer, University of Basel, Department of Physics, tel. +41 61 267 37 24, email: ernst.meyer@unibas.ch
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/Physicists-Measure-van-de…












