
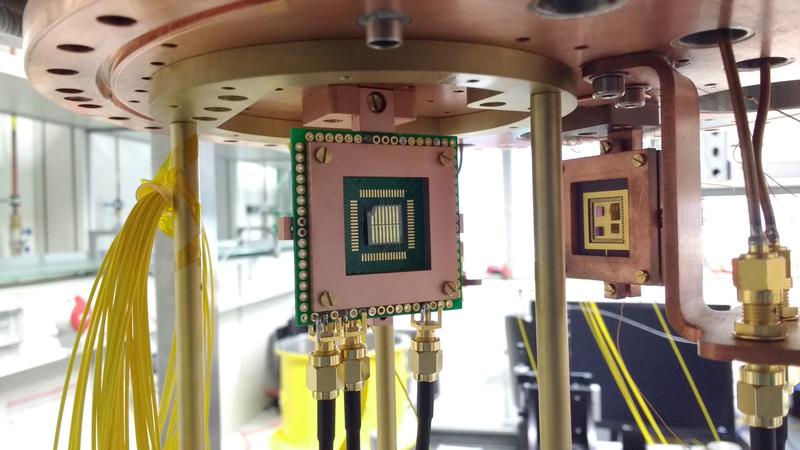
Measurement setup for the characterization of microbridges in a cryostat
Martin Wolff
The development of a quantum computer that can solve problems, which classical computers can only solve with great effort or not at all – this is the goal currently being pursued by an ever-growing number of research teams worldwide.
The reason: Quantum effects, which originate from the world of the smallest particles and structures, enable many new technological applications. So-called superconductors, which allow for processing information and signals according to the laws of quantum mechanics, are considered to be promising components for realizing quantum computers.
A sticking point of superconducting nanostructures, however, is that they only function at very low temperatures and are therefore difficult to bring into practical applications.
Researchers at the University of Münster and Forschungszentrum Jülich now, for the first time, demonstrated what is known as energy quantization in nanowires made of high-temperature superconductors – i. e. superconductors, in which the temperature is elevated below which quantum mechanical effects predominate.
The superconducting nanowire then assumes only selected energy states that could be used to encode information. In the high-temperature superconductors, the researchers were also able to observe for the first time the absorption of a single photon, a light particle that serves to transmit information.
“On the one hand, our results can contribute to the use of considerably simplified cooling technology in quantum technologies in the future, and on the other hand, they offer us completely new insights into the processes governing superconducting states and their dynamics, which are still not understood,” emphasizes study leader Jun. Prof. Carsten Schuck from the Institute of Physics at Münster University.
The results may therefore be relevant for the development of new types of computer technology. The study has been published in the journal “Nature Communications”.
Background and methods:
The scientists used superconductors made of the elements yttrium, barium, copper oxide and oxygen, or YBCO for short, from which they fabricated a few nanometer thin wires. When these structures conduct electrical current physical dynamics called phase slips occur.
In the case of YBCO nanowires fluctuations of the charge carrier density cause variations in the supercurrent. The researchers investigated the processes in the nanowires at temperatures below 20 Kelvin, which corresponds to minus 253 degrees Celsius. In combination with model calculations, they demonstrated a quantization of energy states in the nanowires.
The temperature at which the wires entered the quantum state was found at 12 to 13 Kelvin – a temperature several hundred times higher than the temperature required for the materials normally used.
This enabled the scientists to produce resonators, i.e. oscillating systems tuned to specific frequencies, with much longer lifetimes and to maintain the quantum mechanical states for longer. This is a prerequisite for the long-term development of ever larger quantum computers.
Absorption of a single photon in high-temperature superconductors
Further important components for the development of quantum technologies, but potentially also for medical diagnostics, are detectors that can register even single-photons. Carsten Schuck's research group at Münster University has been working for several years on developing such single-photon detectors based on superconductors.
What already works well at low temperatures, scientists all over the world have been trying to achieve with high-temperature superconductors for more than a decade. In the YBCO nanowires used for the study, this attempt has now succeeded for the first time. “Our new findings pave the way for new experimentally verifiable theoretical descriptions and technological developments,” says co-author Martin Wolff from the Schuck research group.
Participating institutions and funding:
The superconducting films produced at Forschungszentrum Jülich were nanostructured in Jülich and at the University of Münster, where also the experimental characterization was carried out. The study received financial support from the Ministry of Economics, Innovation, Digitization and Energy of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia and the Ernst Ruska-Centre for Microscopy and Spectroscopy with Electrons (ER-C) of the Forschungszentrum Jülich.
Jun. Prof. Carsten Schuck (University of Münster)
Phone: +49-(0)251-83-63948
carsten.schuck@uni-muenster.de
M. Lyatti et al. (2019): Energy-level quantization and single-photon control of phase slips in YBa2Cu3O7–x nanowires. Nature Communications; DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-14548-x
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-14548-x Original publication in “Nature Communications”
https://www.uni-muenster.de/Physik.PI/Schuck/team/team.html Research group Carsten Schuck at Münster University
https://www.uni-muenster.de/forschung/en/profil/schwerpunkt/nanowissenschaften.h… Research focus “Nanosciences” at Münster University












