
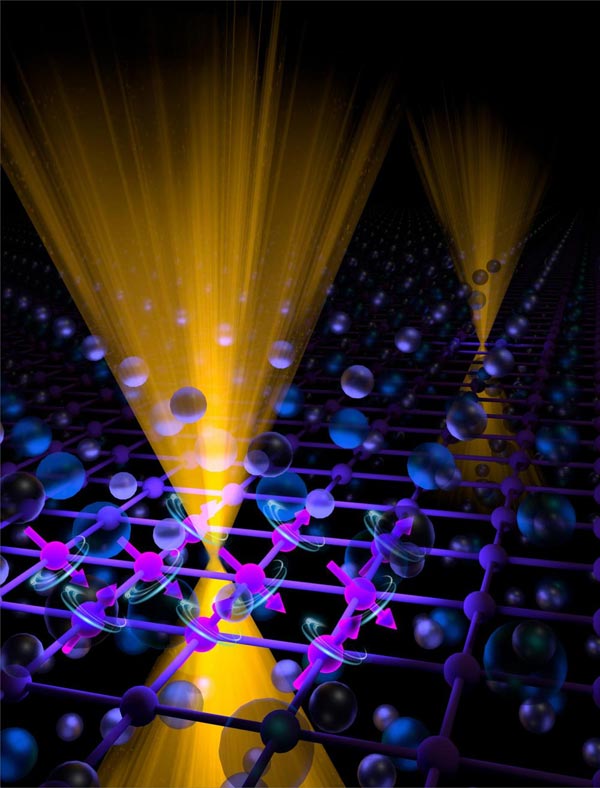
The magnetic and electronic states of newly discovered Sr1-yMn1-zSb2 are depicted by spheres representing the positions of the atoms in the crystal structure of this material with strontium (Sr) depicted by the small violet spheres; antimony (Sb) by the large blue spheres; and manganese (Mn) by the purple spheres. The arrows attached to the Mn atoms represent the magnetic moments of these atoms which align in the orientation shown to give the magnetic properties of Sr1-yMn1-zSb2. Also depicted are the energy and momentum states of the conducting electrons, or charge carriers, which have a Dirac-like dispersion relation shown in gold.
Credit: Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Researchers in the Louisiana Consortium for Neutron Scattering, or LaCNS, led by LSU Department of Physics & Astronomy Chair and Professor John F. DiTusa and Tulane University Professor Zhiqiang Mao, with collaborators at Oak Ridge National Lab, the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Florida State University, and the University of New Orleans, recently reported the first observation of this topological behavior in a magnet, Sr1-yMn1-zSb2 (y, z < 0.1). These results were published this week in Nature Materials (doi:10.1038/nmat4953).
“This first observation is a significant milestone in the advancement of novel quantum materials and this discovery opens the opportunity to explore its consequences. The nearly massless behavior of the charge carriers offers possibilities for novel device concepts taking advantage of the extremely low power dissipation,” DiTusa said.
The phrase “topological materials” refers to materials where the current carrying electrons act as if they have no mass similar to the properties of photons, the particles that make up light. Amazingly, these electronic states are robust and immune to defects and disorder because they are protected from scattering by symmetry.
This symmetry protection results in exceedingly high charge carrier mobility, creating little to no resistance to current flow. The result is expected to be a substantial reduction in heat production and energy saving efficiencies in electronic devices.
This new magnet displays electronic charge carriers that have almost no mass. The magnetism brings with it an important symmetry breaking property – time reversal symmetry, or TRS, breaking where the ability to run time backward would no longer return the system back to its starting conditions.
The combination of relativistic electron behavior, which is the cause of much reduced charge carrier mass, and TRS breaking has been predicted to cause even more unusual behavior, the much sought after magnetic Weyl semimetal phase. The material discovered by this collaboration is thought to be an excellent one to investigate for evidence of the Weyl phase and to uncover its consequences.
###
The researchers involved include J.Y. Liu, J. Hu, Y.L. Zhu, G.F. Cheng, X. Liu, J. Wei, and Z.Q. Mao (Tulane University, New Orleans); Q. Zhang, W. A. Phelan, and J. F. DiTusa (Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge); D. Graf, (National High Magnetic Field Lab, Tallahassee); Q. Zhang, H.B. Cao and D. A. Tennant (Oak Ridge National Laboratory); S.M.A. Radmanesh, D.J. Adams, and L. Spinu (University of New Orleans); Marcelo Jaime and Fedor Balakirev (Condensed Matter and Magnet Science, MPA-CMMS); and I. Chiorescu (NHFML and Florida State University, Tallahassee).














