
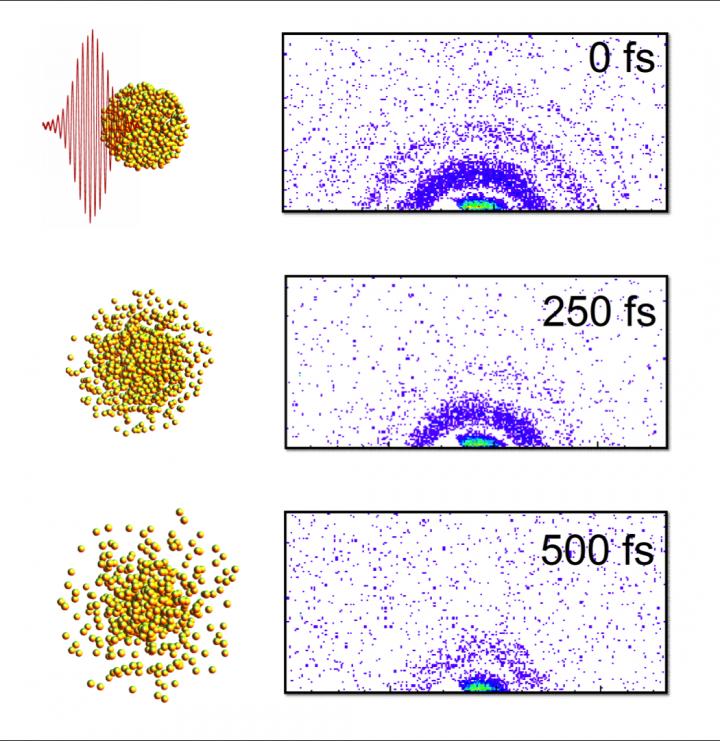
Here are "stills" from an X-ray "movie" of an exploding nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is superheated with an intense optical pulse and subsequently explodes (left). A series of ultrafast x-ray diffraction images (right) maps the process and contains information how the explosion starts with surface softening and proceeds from the outside in.
Credit: Christoph Bostedt
An international team of researchers led by X-ray scientist Christoph Bostedt of the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and Tais Gorkhover of DOE's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory used two special lasers to observe the dynamics of a small sample of xenon as it was heated to a plasma.
Bostedt and Gorkhover were able to use the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) at SLAC to make observations of the sample in time steps of approximately a hundred femtoseconds – a femtosecond being one millionth of a billionth of a second. The exposure time of the individual images was so short that the quickly moving particles in the gas phase appeared frozen.
“The advantage of a machine like the LCLS is that it gives us the equivalent of high-speed flash photography as opposed to a pinhole camera,” Bostedt said. The LCLS is a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
The researchers used an optical laser to heat the sample cluster and an X-ray laser to probe the dynamics of the cluster as it changed over time. As the laser heated the cluster, the photons freed electrons initially bound to the atoms; however, these electrons still remained loosely bound to the cluster.
By imaging exploding nanoparticles, the team was able to make measurements of how they change over time in extreme environments. “Ultimately, we want to understand how the energy from the light affects the system,” Gorkhover said.
“There are really no other techniques that give us this good a resolution in both time and space simultaneously,” she added. “Other methods require us to take averages over many different 'exposures,' which can obscure relevant details. Additionally, techniques like electron microscopy involve a substrate material that can interfere with the behavior of the sample.”
According to Bostedt, the research could also impact the study of aerosols in the environment or in combustion, as the dual-laser “pump and probe” model could be adapted to study materials in the gas phase. “Although our material goes from solid to plasma very quickly, there are other types of materials you could study with this or a similar technique,” he said.
An article based on the study, “Femtosecond and nanometer visualization of structural dynamics in superheated nanoparticles,” appeared as advanced online publication of the February issue of Nature Photonics.
###
The work was funded by the DOE's Office of Science. Tais Gorkhover is the recipient of a Peter Paul Ewald Fellowship from the Volkswagen Foundation.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit the Office of Science website.
For more information, contact Jared Sagoff at jsagoff@anl.gov or 630-252-5549.












