
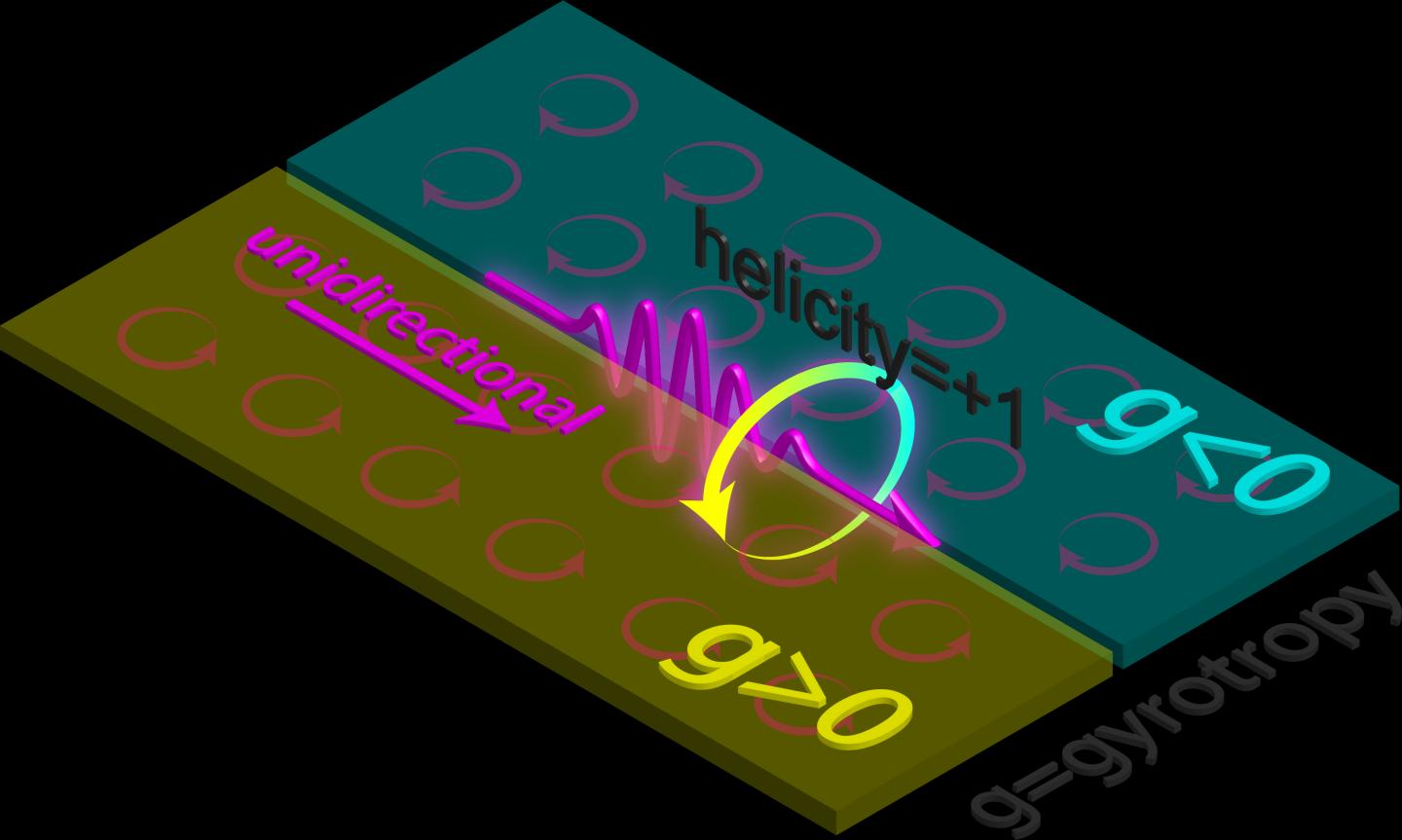
This is an interface of gyrotropic media.
Credit: Zubin Jacob
Researchers at Purdue University have created a quantum spin wave for light. This can be a carrier of information for future nanotechnologies but with a unique twist: they only flow in one direction.
The article “Unidirectional Maxwellian spin waves”, by Todd Van Mechelen and Zubin Jacob has been published in the open access journal Nanophotonics on degruyter.com.
Information technologies at the nanoscale rely on manipulating particles such as electrons and photons. The electron, which is the carrier of charge (electricity), is a fermion while the photon, which is the long-distance transmitter of information, is a boson.
The most important difference between a fermion and a boson is literally how they “spin”. Even though electron spin is widely utilized in commercial nanotechnologies such as magnetic memories, optical spin has only recently become a fundamental degree of freedom in nanophotonics with possible applications in fiber optics, plasmonics, resonators and even quantum metrology.
This explosion of research into optical spin is due to the remarkable features of strongly confined electromagnetic waves. At the nanoscale, spin and direction of motion of light are intrinsically locked to one another.
The researchers used many designs to achieve this behavior, in particular, an interface of mirror symmetric gyrotropic media, illustrated in the accompanying figure. Gyrotropy is a form of material response to light waves that transfer spinning behavior of electrons to photons (shown by circular arrows).
“Our research opens up the possibility of new applications where devices communicate information in one direction but block it completely in the reverse. This is important for the safe functioning of high power devices as well as for reducing interference between transmitted/received electromagnetic signals from cellphone antennas,” said Zubin Jacob.












