
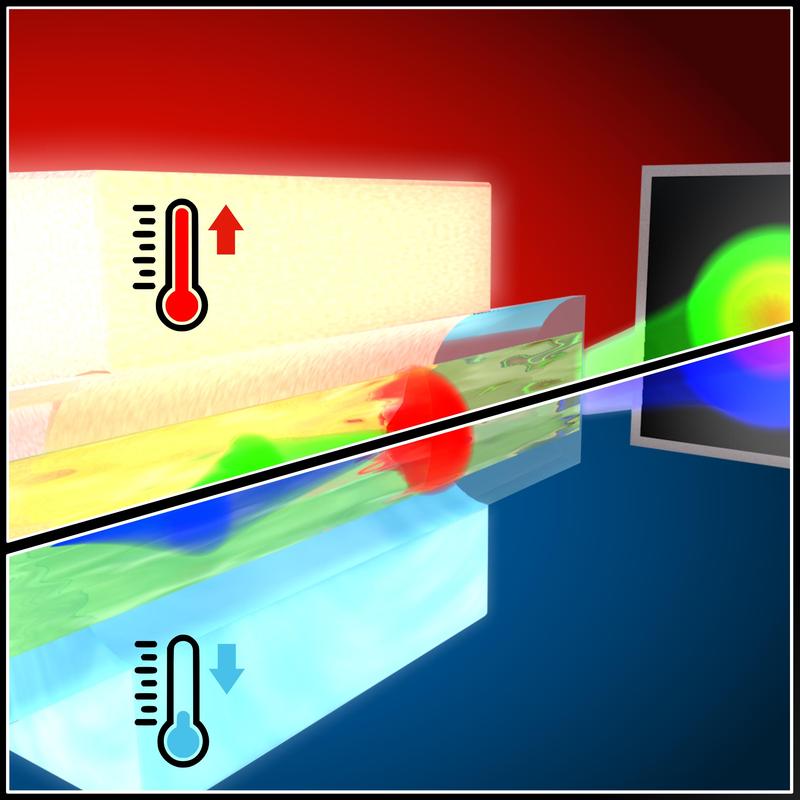
Schematic representation of the temperature-controlled supercontinuum generation.
Source: Leibniz-IPHT
Already last year, the researchers provided experimental proof of a new dynamic of hybrid solitons– temporally and spectrally stationary light waves resulting from the unique characteristics of the carbondisulfide-filled fiber core.
Now they succeeded to control light generation and the propagation of the wave packages via temperature and pressure tuning along the optical fiber.
In this way, they realised near and mid-infrared supercontinuum light sources with flexibly adjustable spectral band width for applications in medical imaging, measurement technology, and spectroscopy.
“Our computer simulations and experiments showed that the wavelength of the initial solitons remains constant over the whole temperature range. The dispersive wave packages resulting from soliton fission, indeed exhibit spectral shifts depending on the ambient temperature.
A temperature change of only 13 Kelvin allows us to adjust the band width of radiation over several hundred nanometers“, explains Mario Chemnitz, scientist at Leibniz-IPHT and first author of the publication.
The original article “Thermodynamic control of soliton dynamics in liquid-core fibers“ by Mario Chemnitz, Ramona Scheibinger, Christian Gaida, Martin Gebhardt, Fabian Stutzki, Sebastian Pumpe, Jens Kobelke, Jens Limpert, Andreas Tünnermann and Markus A. Schmidt was published 29th May 2018 in Optica. The research work was funded by the German Research Foundation and the Freestate of Thuringia.
https://www.leibniz-ipht.de/en/institute/presse/news/detail/temperaturgesteuerte…
https://www.osapublishing.org/optica/abstract.cfm?uri=optica-5-6-695












