Earthquake Study by Scripps Scientists Produces New Depiction of Fault Zones
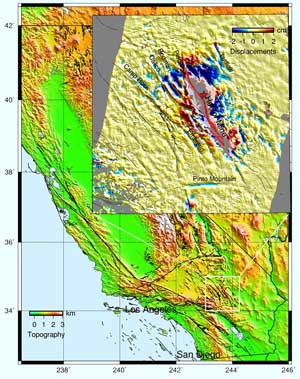
A geographic depiction of the Eastern California Shear Zone. The inset, displaying data from synthetic aperture radar interferometry (InSAR), shows the deformation induced by the 1999 Hector Mine earthquake on nearby faults. <br>© Scripps
Analysis uncovers unusual earthquake-related deformation, paves the way for methods to identify new active faults
On Oct. 16, 1999, approximately 37 miles from Palm Springs, Calif., a magnitude 7.1 earthquake ripped through 28 miles of faults in the Mojave Desert. Because of the area’s sparse population and development, the massive quake caused virtually no major measurable injuries or destruction.
Yet the “Hector Mine” event, named after a long-abandoned mine in the area, has produced a treasure of information about earthquakes, faults, and ruptures for scientists at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego. ANIMATION
In results published in the Sept. 13 issue of Science, the scientists, along with a colleague at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), reveal that they used satellite and radar technologies to uncover never-before documented characteristics of faults. These include the first evidence that faults move backwards, contrary to conventional observations, and indications that the material within faults is significantly different than its surroundings.
Scripps’s Yuri Fialko, the lead author of the study, says the implications of the study include providing a new way to identify potentially active faults, helping to track when the last earthquake occurred in a fault zone, and perhaps better understanding the earthquake process.
Fialko calls the Hector Mine event the “perfect” earthquake for the satellite and radar technologies that he and his colleagues used.
It is the first event comprehensively imaged using interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR), as Fialko and coauthors demonstrated in an earlier study published in Geophysical Research Letters. InSAR uses a series of satellite recordings to detect changes in Earth’s surface.
According to Science study coauthor David Sandwell, the fresh data gave researchers an uncommon and immediate window into earthquake processes in fault areas that are only typically imaged after being altered by natural forces such as rainstorms and unnatural forces such as off-road vehicle disruption.
Fialko, Sandwell, and coauthors Duncan Agnew, Peter Shearer, and Bernard Minster of Scripps, and Mark Simons of Caltech, studied the information to find unusual signatures of fault displacements caused by Hector Mine in the Eastern California Shear Zone (ECSZ) in an area thought to be relatively inactive.
The most surprising finding was the first evidence that faults can move backwards. Prior to an earthquake, faults are locked in position by the “glue” of friction. Changes due to energy released during earthquakes cause faults to move.
“Even small stress perturbations from distant earthquakes can cause faults to move a little bit, but it’s only been known to cause this motion in a forward sense,” said Fialko. “Here we observed the faults coming backwards due to relatively small stress changes, which is really quite unusual.”
The study argues that the backward motion on the faults is caused by the dissimilar material within the faults, rather than the frictional failure.
“We used an analysis model that effectively says that material within the faults is mechanically distinct from the material surrounding the faults,” said Fialko, of the Cecil H. and Ida M. Green Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics at Scripps. “The rocks within the faults appear to be softer.”
He says the fault zones become strained during periods of stress, acting like a soft, sponge-like material. The soft area thus becomes squeezed during periods of energy release.
According to Fialko, the results will guide new seismic studies to areas with contrasting fault material, such as that seen in the Eastern California Shear Zone. They can then be used as a way of identifying potentially active faults.
Another possibility emerges through studying the properties of fault zones over time.
“Measurements of changes in the mechanical properties of faults may yield valuable information about the earthquake cycle. For example, we might be able to say how long it was before the fault experienced an earthquake and how long it takes to heal,” said Fialko.
Coauthor Shearer attributes these detailed results to the “breakthrough” offered by InSAR technology.
“Prior to InSAR, all we had were spot measurements of the deformation field,” said Shearer. “At best we had maybe a few hundred points across southern California. You had a point here and there so you didn’t really know what was happening. With InSAR we have millions of points and thus a continuous picture of deformation across southern California.”
The scientists say the findings became possible due to highly successful satellite missions of the European Space Agency.
“We hope that NASA will launch the U.S. InSAR satellites to monitor surface changes in California and elsewhere,” Fialko said. “This will dramatically improve our ability to study earthquakes as well as other potentially hazardous phenomena, such as volcanic activity and man-made deformation.”
The research was supported by the Southern California Earthquake Center and the National Science Foundation (NSF). Synthetic aperture radar data were purchased with funding from NASA, the U.S. Geological Survey, and NSF.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://scrippsnews.ucsd.edu/pressreleases/fialko_science_faults.htmlAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



