Rice deciphers optical spectra of carbon nanotubes
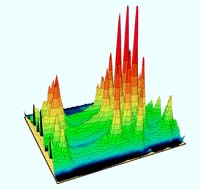
This three-dimensional plot of light-emission intensity of carbon nanotubes shows a peak for each "species" of light-emitting nanotube, indicating that each "species" has a unique optical signature. Variations in signature are due to slight differences in nanotube structure and diameter. Emission intensity is plotted as a function of excitation wavelength and emission wavelength <br>
Study opens door for faster, simpler methods of measuring carbon nanotubes
Building upon this summer’s groundbreaking finding that carbon nanotubes are fluorescent, chemists at Rice University have precisely identified the optical signatures of 33 “species” of nanotubes, establishing a new methodology for assaying nanotubes that is simpler and faster than existing methods.
In research published this week by Science magazine, a spectroscopy research team led by Rice Chemistry Professor R. Bruce Weisman detailed the wavelengths of light that are absorbed and emitted by each type of light-emitting nanotube. The findings hold great promise for chemists, physicists and materials scientists studying nanotubes, because it otherwise takes many hours of tedious testing for researchers to assay a single sample of nanotubes, and optical tests could be much faster and simpler.
“Optical nanotube spectroscopy is an important enabling tool for nanotechnology research, because it reveals the composition of nanotube samples through simple measurements,” said Weisman. “Chemists and biochemists commonly use optical instruments that can characterize samples within a matter of seconds. With refinement, similar methodologies can probably be applied to nanotube analysis.”
Carbon nanotubes are cylinders of carbon atoms that measure about one nanometer, or one-billionth of a meter, in diameter. That’s about 50,000 times smaller than a human hair. Because of their astounding physical and electrical properties, scientists have envisioned using nanotubes in everything from the skins of spacecraft to electronic wiring that’s 100 times smaller than the circuits in today’s most advanced silicon microchips.
The ability to sort nanotubes must be overcome if they are to be transformed from a laboratory oddity to a marketable commodity, but sorting isn’t feasible until chemists have a practical way to inspect what they’re sorting. Sorting is an issue because nanotubes aren’t identical. There are actually three families of carbon nanotubes, and cousins and siblings in these families have slightly different diameters and physical structures. While almost imperceptible, these slight variations give rise to drastically different properties: about one-third of nanotubes are metals for example, and the others are semiconductors. Since every method of preparing nanotubes yields dozens of varieties, researchers have to sort and classify the types of tubes they are most interested in studying.
This summer, Weisman’s group and the carbon nanotube research team of Rice’s Richard Smalley reported that all semiconducting varieties of nanotubes fluoresce. Fluorescence occurs when a substance absorbs one wavelength of light and emits a different wavelength in response.
Once fluorescence of nanotubes was confirmed, researchers in Weisman’s and Smalley’s research groups began investigating the spectral properties of various kinds and classes of nanotubes. The research is detailed in a paper titled “Structure-Assigned Optical Spectra of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes,” published online today by Science magazine.
In addition to applied researchers, theoretical scientists will also use the spectral research to help refine models that predict the expected physical, mechanical, structural and electrical properties of nanotubes. In several instances, Weisman’s group reported experimental data that differed substantially from what theorists have predicted.
###
The Rice research team also included Sergei M. Bachilo, Michael S. Strano, Carter Kittrell, Robert H. Hauge and Smalley. The research was funded by the National Science Foundation and the Robert A. Welch Foundation.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://chico.rice.edu/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



