NASA eyes Tropical Storm Nock-Ten's heavy rains for Hainan Island and Vietnam
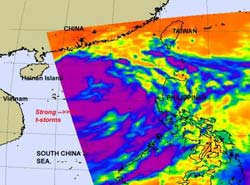
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the eastern side of Tropical Storm Nock-ten and the AIRS instrument captured this infrared image of the storm's cold cloud tops (purple) and strong thunderstorms on July 28 at 0517 UTC (1:47 a.m. EDT). Hainan Island, China is located to the west and can be seen on the left side of the image. Credit: NASA/JPL, Ed Olsen<br>
Bands of strong thunderstorms that make up tropical storm Nock-ten were visible in an infrared image captured on July 28 by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite. The colder the cloud tops, the higher the thunderstorms and the stronger they are, and cloud top temperatures over a large area of Nock-ten were colder than -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius) and the cloud tops likely extended into the tropopause. High, strong thunderstorms like those also can generate heavy rainfall, up to 2 inches (50 mm) per hour. Those in Nock-ten's path can expect heavy rainfall, local flooding, gusty winds and rough surf along coastal areas.
AIRS imagery has shown that the convection within Nock-ten has intensified as it moves through the warm waters of the South China Sea. It is expected to strengthen a little more with the warm sea surface temperatures feeding it, and wind shear remaining light.
On July 28, at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) Tropical Storm Nock-ten was already raining on Hainan Island and headed toward another landfall in Vietnam. Its center was still 464 nautical miles east-southeast of Hanoi, Vietnam near 18.2 North and 113.0 East. Nock-ten's sustained winds are near 55 knots (63 mph/101 kmh) and it is moving in a westerly direction at 12 knots (14 mph/22 kmh).
The Joint Typhoon Warning center forecasters expect that the center of Nock-ten will make landfall over Hainan Island, China before July 29 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) and weaken a little as it moves over land. However, once it re-emerges over water in the Gulf of Tonkin, it may strengthen a little before making final landfall in Vietnam.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



