Smart swarms of bacteria inspire robotics researchers
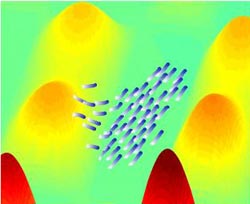
Simulated interacting agents collectively navigate towards a target. Credit: American Friends of Tel Aviv University (AFTAU)<br>
Much to humans' chagrin, bacteria have superior survival skills. Their decision-making processes and collective behaviors allow them to thrive and even spread efficiently in difficult environments.
Now researchers at Tel Aviv University have developed a computational model that better explains how bacteria move in a swarm — and this model can be applied to man-made technologies, including computers, artificial intelligence, and robotics. Ph.D. student Adi Shklarsh — with her supervisor Prof. Eshel Ben-Jacob of TAU's Sackler School of Physics and Astronomy, Gil Ariel from Bar Ilan University and Elad Schneidman from the Weizmann Institute of Science — has discovered how bacteria collectively gather information about their environment and find an optimal path to growth, even in the most complex terrains.
Studying the principles of bacteria navigation will allow researchers to design a new generation of smart robots that can form intelligent swarms, aid in the development of medical micro-robots used to diagnose or distribute medications in the body, or “de-code” systems used in social networks and throughout the Internet to gather information on consumer behaviors. The research was recently published in PLoS Computational Biology.
A dash of bacterial self-confidence
Bacteria aren't the only organisms that travel in swarms, says Shklarsh. Fish, bees, and birds also exhibit collective navigation. But as simple organisms with less sophisticated receptors, bacteria are not as well-equipped to deal with large amounts of information or “noise” in the complex environments they navigate, such as human tissue. The assumption has been, she says, that bacteria would be at a disadvantage compared to other swarming organisms.
But in a surprising discovery, the researchers found that computationally, bacteria actually have superior survival tactics, finding “food” and avoiding harm more easily than swarms such as amoeba or fish. Their secret? A liberal amount of self-confidence.
Many animal swarms, Shklarsh explains, can be harmed by “erroneous positive feedback,” a common side effect of navigating complex terrains. This occurs when a subgroup of the swarm, based on wrong information, leads the entire group in the wrong direction. But bacteria communicate differently, through molecular, chemical and mechanical means, and can avoid this pitfall.
Based on confidence in their own information and decisions, “bacteria can adjust their interactions with their peers,” Prof. Ben-Jacob says. “When an individual bacterium finds a more beneficial path, it pays less attention to the signals from the other cells. But at other times, upon encountering challenging paths, the individual cell will increase its interaction with the other cells and learn from its peers. Since each of the cells adopts the same strategy, the group as a whole is able to find an optimal trajectory in an extremely complex terrain.”
Benefitting from short-term memory
In the computer model developed by the TAU researchers, bacteria decreased their peers' influence while navigating in a beneficial direction, but listened to each other when they sensed they were failing. This is not only a superior way to operate, but a simple one as well. Such a model shows how a swarm can perform optimally with only simple computational abilities and short term memory, says Shklarsh, It's also a principle that can be used to design new and more efficient technologies.
Robots are often required to navigate complex environments, such as terrains in space, deep in the sea, or the online world, and communicate their findings among themselves. Currently, this is based on complex algorithms and data structures that use a great deal of computer resources. Understanding the secrets of bacteria swarms, Shklarsh concludes, can provide crucial hints towards the design of new generation robots that are programmed to perform adjustable interactions without taking up a great amount of data or memory.
American Friends of Tel Aviv University (www.aftau.org) supports Israel's leading, most comprehensive and most sought-after center of higher learning. Independently ranked 94th among the world's top universities for the impact of its research, TAU's innovations and discoveries are cited more often by the global scientific community than all but 10 other universities.
Internationally recognized for the scope and groundbreaking nature of its research and scholarship, Tel Aviv University consistently produces work with profound implications for the future.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.aftau.orgAll latest news from the category: Interdisciplinary Research
News and developments from the field of interdisciplinary research.
Among other topics, you can find stimulating reports and articles related to microsystems, emotions research, futures research and stratospheric research.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



