New calculations solve an old problem with DNA
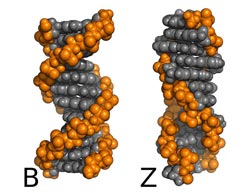
The normal (B-form) DNA will switch to left-handed (Z-form) DNA when it is physically twisted, or when a lot of salt is added to the solution. Researchers at the University of Luxembourg were able to accurately calculate for the first time the amount of salt which is required to do this.<br>Josh Berryman<br>
Researchers at the University of Luxembourg were able to accurately calculate for the first time the amount of salt which is required to do this. Z-DNA in the cell leads to loss of function and cancer.
It has been known since the seventies that excessive salt causes DNA to reverse its twist, from a right-handed spiral to a left-handed one. DNA in the Z form is treated by our natural repair enzymes as damaged, and is therefore usually deleted from the cell. Deletion of genetic material can lead to cancer or to other problems, so the B-Z transition is no mere curiosity. However such is the complexity of the DNA molecule that a theoretical explanation which correctly predicts the amount of salt to do this has never before been found.
Dr. Josh Berryman and Professor Tanja Schilling of the University of Luxembourg have now been able to find a method of calculation which predicts this transition with unprecedented accuracy. With this success in describing the most enigmatic of molecules, the team is optimistic that they will be able to perform similar mathematical analyses for a variety of other substances.
“It will enable us to predict material properties such as melting temperatures or elasticity. And this will be done with high accuracy using our new technique. Hence, we can now design new materials and biomaterials on the computer more effectively than before,” said Prof. Schilling.
Prof Schilling and Dr Berryman are physicists at the University’s Physics and Material Sciences Research Unit, which comprises a team of 50 researchers.
The paper entitled “Free Energies by Thermodynamic Integration Relative to an Exact Solution, Used to Find the Handedness-Switching Salt Concentration for DNA” was published in the Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


