A scanner for hereditary defects
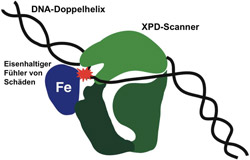
The XPD scanner (green) in close contact with a damaged point (red) on the DNA double helix. The damaged DNA strand lies in a deep pocket of the protein to enable a ferrous sensor (Fe) to come into contact with the damaged point, thereby halting the protein as it moves along the DNA.<br>Picture: UZH<br>
One of these proteins works like a scanner, continually scouring the genetic material for signs of damage. Researchers from the Institute of Veterinary Pharmacology and Toxicology at the University of Zurich see new possibilities in this damage recognition for improving cancer treatment in humans.
Our DNA is constantly under attack from UV light, toxins and metabolic processes. Proteins and enzymes continually repair the damaged DNA. Unrecognized and therefore unrepaired damage to the genetic material, however, accelerates aging and causes cancer and genetic disorders. A team headed by veterinary pharmacologist and toxicologist Hanspeter Nägeli has now discovered that the protein XPD plays a key role in locating damaged DNA.
XPD protein as scanner
Genetic information is stored on approximately three billion base pairs of adenine/thymine or cytosine/guanine in the thread-like DNA double helix. The researchers reveal that the XPD protein works like a scanner that glides along the DNA double helix, scouring the bases for signs of damage. As soon as one of the protein’s ferrous sensors encounters damage as it moves along, it is stopped, thereby marking damaged spots in need of repair. Besides patching up DNA, XPD is also involved in cell division and gene expression, thus making it one of the most versatile cell proteins.
Basis for possible courses of therapy
While repairing the DNA protects healthy body tissue from damage to the genetic material, however, it diminishes the impact of many chemotherapeutic substances against cancer. “Damage recognition using XPD opens up new possibilities to stimulate or suppress DNA repair according to the requirements and target tissue,” explains Hanspeter Nägeli. The results could thus aid the development of new cancer treatments.
Literature:
Nadine Mathieu, Nina Kaczmarek, Peter Rüthemann, Andreas Luch, Hanspeter Naegeli. DNA quality control by a lesion sensor pocket of the xeroderma pigmentosum group D helicase subunit of TFIIH. Current Biology. January 24, 2013. doi: 10.1016/
Contacts:
Prof. Dr. Hanspeter Nägeli
Institute of Veterinary Pharmacology and Toxicology
University of Zurich
Phone: +41 44 635 87 63
E-mail: naegelih@vetpharm.uzh.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uzh.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



