INEEL researchers develop medical imagery breakthrough
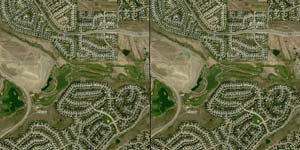
Digitally altered Denver suburb <br> <br>Although these two images of a Denver suburb look virtually identical when compared side by side, some details have been digitally altered for illustration. Although most people can spot the lake and building missing from one photo (middle left), the Change Detection System (CDS) program immediately reveals that a swimming pool (lower right neighborhood) and a dirt track (upper right field) are also absent from one of the images. The large photo below has graphic highlights in yellow to emphasize the changes that CDS software makes visible. (Photo by Space Imaging®, Digital Airborne Imaging System)
System detects tissue changes
Mammograms, X-rays and other pricey medical scans do little good if doctors can’t see the tiny changes that signal early stages of disease. But such warning signs are often too subtle to spot by eye, and too complex for computers to interpret. Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory have developed the Change Detection System, technology that highlights slight differences between digital images. In fact, lead researcher Greg Lancaster convinced doctors of the program’s power when he used it to compare scans of his own brain after he’d had a tumor removed. One medical technology firm is already looking to license the program.
This medical advance is a direct result of applying national security technology, which was initiated through funding from the DOE’s Applied Technology Program. The CDS software is so quick, easy and affordable that it now boasts a spot among the 100 most technologically significant products introduced in the past year. R&D Magazine editors notified the winners in July and will feature the winning products in the September issue.
Medical imaging often involves comparing side-by-side images to see if changes have emerged. But discerning minuscule differences between two pictures can be nearly impossible. Computers even struggle with the task, laboriously scrutinizing each pixel and often finding only trivial differences in camera angle.
In the past, the best technology available for comparing images has been the flip-flop technique, which capitalizes on the visual reflex that draws our eyes toward motion. Rapidly alternating between two similar digital images on a screen creates an animation effect where identical elements seem stationary and differences appear as movement. But the flip-flop approach requires that both pictures be shot from the exact same position using a mounted camera. Since stationary cameras are impractical in many cases, flip-flop comparisons are often impossible.
Now, the CDS technology developed by the INEEL’s Lancaster, James Litton Jones and Gordon Lassahn combines the strengths of rote computer analysis with the powerful human reflex elicited by the flip-flop technique. The CDS program aligns images, to within a fraction of a pixel, from hand-held or otherwise imprecise cameras. The alignment compensates for differences in camera angle, height, zoom or other distractions that previously confounded flip-flop comparisons.
Flipping between two seemingly identical images aligned by CDS reveals once imperceptible differences–tiny retinal changes signal macular degeneration, small earthen shifts herald hill erosion, footprints appear in a gravel road. The alignment process takes only seconds and the software is simple enough to be operated by a 10-year-old child. What’s more, the 350 KB program can operate on a standard PC or even a handheld computer.
Such versatility makes the program attractive to everyone from security guards to working parents, field researchers to physicians. Potential applications for this technology include surveillance (detect whether doors have been opened or cars have been moved), forensics (compare tire prints or fingerprints), national security (reveal tampering with container locks and seals), home security (divulge whether drawers or rooms were disturbed), and field research (monitor environmental changes). And the medical applications became clear to Lancaster as he grappled with a brain tumor during research for the CDS project.
After doctors removed the growth, they monitored Lancaster’s brain with twice yearly MRI scans to make sure the tumor didn’t return. As his physicians squinted at the images, searching for the tiniest change, Lancaster worried they might miss something.
“They just stare at them to try to find differences,” said Lancaster. “I said, ’Man, that’s so archaic,’” Lancaster decided to test his doctors’ powers of perception with and without CDS.
“I took an image, altered it ever so slightly, brought in both pictures and said, ’Can you see a difference?’ They looked at the two images and admitted, ’Well, no,’” Lancaster said. “But with the flip-flop method, it really pops out. They said, ’Wow! What a tool!’”
As CDS hits the marketplace, it joins 28 previous R&D 100 winners developed at INEEL in the last 18 years. This is the 7th year in a row that INEEL has won a spot in the R&D 100 ranking.
The INEEL is a science-based, multiprogram national laboratory dedicated to supporting the U.S. Department of Energy’s missions in environment, energy, science and national defense. The INEEL is operated for the DOE by Bechtel BWXT Idaho, LLC.
Additional information on CDS, including photo illustrations, can be seen by visiting http://www.inel.gov.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



