International team observe 'hungry twin' stars gobbling their first meals
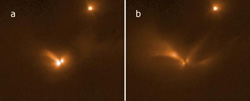
Hubble Space Telescope 1.6 micron images taken at two epochs corresponding to pulse phases of 0 (a) and 0.3 (b). North is up and east is to the left. LRLL 54361 is the extended source to the lower left; the point source at upper right is another young star, LRLL 1843. The light from LRLL 54361 subtends roughly 14” (~4000 AU at the distance of the IC 348 region) in (a), and about 50” (~15,000 AU) in (b). Most if not all of this light is likely the result of scattering of circumstellar dust in the protostellar envelope. An apparent edge-on disk is visible in the center, and 3 separate structures indicative of outflow cavities extend to the northwest, southwest, and northeast. The extent and morphology of the scattered light changes substantially between epochs as a result of the propagation of the pulse peak light. Photo courtesy of Robert Gutermuth<br>
Now a team of astronomers including Robert Gutermuth, a University of Massachusetts Amherst expert in imaging data from the Spitzer Space Telescope, reports observing an unusual “baby” star that periodically emits infrared light bursts, suggesting it may be twins, that is, a binary star. The discovery is reported this month in Nature.
The extremely young object, dubbed LRLL 54361, is about 100,000 years old and is located about 950 light years away toward the Perseus constellation. Years of monitoring its infrared with the Spitzer instrument reveal that it becomes 10 times brighter every 25.34 days, Gutermuth and colleagues say. This periodicity suggests that a companion to the central forming star is likely inhibiting the infall of gas and dust until its closest orbital approach, when matter eventually comes crashing down onto the protostellar “twins.”
Gutermuth, who surveys star-forming molecular clouds with Spitzer to search for protostars, says, “The idea that this object is a baby binary system fits our data, so, twins fit our data. In single protostars, we would still see matter dumping onto the star non-uniformly, but never with the regularity or intensity of the bursts we observe in LRLL 54361. The 25.43-day period is consistent with the orbital period we would expect from a very close binary star.”
The protostar twins, embedded in a gas “cocoon” many times larger than our solar system, offer an unusual chance to study what looks like a developing binary star system, he adds. Because dense envelopes of gas and dust surround embryonic stars, the only detectable light to escape is at longer, infrared wavelengths. “Spitzer’s infrared camera is perfect for penetrating this cool dust to detect emission from the warm center,” says Gutermuth.
“When you have two young stars feeding from the same circumstellar disk, the gravitational influence of the secondary companion can cause hiccups, an inhibition of infalling material from the disk. But when the orbital paths approach closely, that material can rush in, triggering feeding pulses for both stars and releasing a bright burst of light. The flash moves out from the center, reflecting off the disk and cavities in the envelope like an echo reverberating out from cave walls. We’ve seen the light flashes with Spitzer and have imaged the echo-tracing cavities in its envelope with the Hubble Space Telescope.”
The light echo to which Gutermuth refers is seen in images taken at the near-infrared limit of the Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 instrument. The lead investigator for this work and the Spitzer study is UMass Amherst alumnus James Muzerolle, now of the Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore. The investigators are careful to point out that they’re not sure what is at the center of object LRLL 54361, but if it is an embryonic binary star, the prospects are exciting.
Scientists have shown that close binary low mass stars are a somewhat rare outcome of the star formation process. But understanding their formation is critical to address some of the fundamental open questions in star and planet formation, such as how protostars form, how they accumulate their mass and how planets form from their circumstellar disks, Gutermuth points out. It’s believed that most of a central star’s mass is assembled early, whereas planet formation in spinning outer gaseous disks may take several million years to complete.
Another reason this object is so interesting, he says, is that it provides a new demonstration of the impact of time-domain astronomy. “By analyzing the variability of this object’s light over time, we have obtained a unique set of constraints on its physical nature. This system offers us a rare chance to observe the evolution of the disk and envelope around a binary star in almost real time.”
“Looking ahead, we’ll characterize this system further at millimeter wavelengths with the aid of the Large Millimeter Telescope now becoming operational under a partnership between UMass Amherst and Mexico’s Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Óptica y Electrónica. Studying millimeter variability over time will be part of our approach.”
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


