X-ray laser reveals chemical reaction
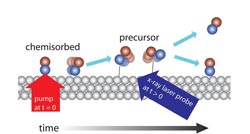
Caption: The x-ray laser investigates the change in the electron structure when CO molecules desorb from a metal surface of ruthenium. Roughly 30% of the molecules are pumped up with the aid of a femtosecond of optic laser from the surface-bonded (“chemisorbed”) state to a transient intermediate state (“precursor”) where they interact faintly with the surface. By examining the molecules with the x-ray laser with varying delay periods, it is possible to show that the time scale for achieving the precursor state is a few picoseconds and that they exist there for a few tens of picoseconds before either leaving the surface entirely or returning to the surface.<br>
The study, published in Science, found, among other things, evidence of a much-discussed intermediate state before molecules bind to or leave a metal surface. The possibility of monitoring at the molecular level how the electron structure changes in a chemical reaction creates entirely new opportunities for investigating and understanding key chemical processes in detail.
“To identify and characterize short-lived intermediate states in chemical reactions on the surface of metals has long been a dream,” says Henrik Öström at the Department of Physics, Stockholm University, who is part of the international research team that carried out the study. “With the new free electron x-ray laser at SLAC, we have shown that dreams can become reality and managed to identify a short-lived intermediate state when the bindings of CO molecules to a metal surface are broken or created.
SLAC (Stanford Linear Accelerator Center) was long a flagship of particle physics, where electrons were accelerated to nearly the speed of light in a three-kilometer-long linear accelerator. Now the accelerator has been rebuilt to generate, instead, powerful ultra-short (10-100 femtosecond) pulses of x-ray beams with a wavelength that makes it possible to examine the surroundings of a molecule down to the level of an individual atom. The pulses are sufficiently short to provide a snapshot of the electron distribution around the atom. By varying the delay between the start of a reaction and when the distribution of electrons is monitored with the x-ray pulse, these scientists can create a suspended-time image of changes in the course of the reaction.
“A first challenge was whether the incredibly powerful pulse would destroy the sample,” explains Anders Nilsson, a professor of synchrotron-light physics at SLAC and an adjunct professor at Stockholm University. “However, it turned out to be entirely possible to adjust the experiment in a way that enabled us to make our measurements.”
In the experiment, CO molecules were dosed onto a metal surface of ruthenium, which is used in automobile catalytic converters, for instance. CO binds strongly to the surface but can be made to let go by heating up the surface, which was done with a pulse from an optical laser. By starting the reaction for all the molecules at the same time, the team got a sufficient number of molecules to simultaneously enter a state where they have almost let go of the surface but still have a weak binding to it. From this short-lived state, the molecules can then continue out into a gas phase or renew their bond when the surface cools down again.
“Scientists have long speculated whether such a state, a so-called ‘precursor,’ exists. The new experiment is the first to directly show its existence,” says Lars G. M. Pettersson at the Department of Physic, Stockholm University. These studies will not go on to more complex reactions of interest to the field of synthetic fuels, among other applications.
Besides the researchers from Stockholm University, scientists from Stanford University, SLAC, the University of Hamburg, the Technical University of Denmark, the Helmholtz Center in Berlin, and the Fritz Haber Institute in Berlin.
Article; Science 15 March 2013: 1302-1305. [DOI:10.1126/science.1231711]
Further information:
Henrik Öström at the Department of Physics, Stockholm University, phone: +46 (0)8 5537 8641 mobile: +46 (0)73 035 9150 e-mail: ostrom@fysik.su.se
Lars G.M. Pettersson at the Department of Physics, Stockholm University, phone: +46 (0)8 5537 8712 mobile: +46 (0)70 495 1990 e-mail: lgm@fysik.su.se
Anders Nilsson at SLAC and Stockholm University, phone: +1 650 926 2233 e-mail: nilsson@slac.stanford.edu
Pressofficer Viktor Sandqvist, e-mail: viktor.sandqvist@su.se, phone +46-767 852 172
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…

Machine learning accelerates catalyst discovery
Conceptual blueprint to analyze experimental catalyst data. Machine learning (ML) models have recently become popular in the field of heterogeneous catalyst design. The inherent complexity of the interactions between catalyst…

More efficient car designs with AI
8,000 open source models for sustainable mobility. Designing new cars is expensive and time consuming. As a result, manufacturers tend to make only minor changes from one model generation to…


