Structure of the Cellular Recycling Bin
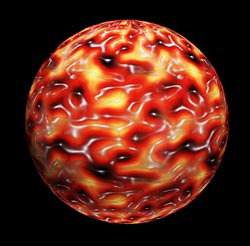
Capture:<br> The picture shows the structure of the autophagic scaffold. The scientists used atomic force microscopy to visualize the hight profile of the scaffold on artificial membranes. The protein meshwork rises gradually (yellow-red) from the ground level of the membrane (black) to the crest of the scaffold (white) where it reaches its maximum hight. The resulting two-dimensional map was then projected onto a sphere which represents the autophagosome. <br>Picture: Thomas Wollert<br>Copyright: MPI of Biochemistry <br>
In a similar way, a cellular waste management system constantly picks up superfluous proteins and damaged organelles in human cells and delivers them to recycling facilities. However, if the cellular waste management system stops working, severe illnesses like Alzheimer´s disease or cancer may develop.
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried near Munich, Germany, recently revealed how a major cellular recycling system – autophagy – works. The results of the study have now been published in the research journal Cell.
The autophagic system in cells captures cellular waste and delivers it to specialized recycling facilities, called lysosomes. Thus autophagy protects the cell from accumulating cell debris. If autophagy slows down or stops working, severe diseases like cancer, Parkinson´s or Alzheimer´s disease may occur.
Much in the same way as trash bags envelop waste, a membrane engulfs cellular debris during autophagy. This molecular “recycling bag” is called autophagosome. After the membrane has been wrapped around the waste, it is transported to lysosomes for degradation. Because lysosomes are also surrounded by membranes, autophagosomes are able to fuse with them to deliver their content without leakage. Finally, an armada of different enzymes degrades the lysosomal content into its basic molecular building blocks.
Cellular waste differs enormously in size and shape, imposing a major challenge for the autophagic system. On the one hand the membrane of autophagosomes needs to be flexible enough to engulf the waste. On the other hand, mechanical stability is needed to guide the membrane around the waste in a zipper-like fashion. Thomas Wollert and his Research Group “Molecular Membrane and Organelle Biology” now revealed the molecular architecture of an autophagic membrane scaffold, which mechanically supports autophagosomes.
Small meshes – large effects
The scaffold is a flat meshwork made of proteins that cover the membrane of the autophagosome entirely. The vertices of the mesh consist of the small protein Atg8 which is attached to the autophagic membrane and serves as a molecular anchor. A second protein complex cross-links Atg8 to build up the scaffold. One mesh is only 16 nm long, i.e. 10.000-fold shorter than a human hair is thick, and the scaffold is only 8 nm thick. When the membrane has entirely enveloped the molecular waste, the scaffold is no longer needed and removed by an enzyme which cuts Atg8 from the membrane.
Furthermore, the researchers were able to recreate the scaffold on artificial membranes in the test tube and to follow its assembly and disassembly in real time. “It is important that we understand the molecular mechanisms that drive autophagy to be able to modulate its speed”, said Thomas Wollert, MPIB group leader who supervised the study. “If we were able to accelerate autophagy, Alzheimer´s disease and other neurological disorders could perhaps be cured in the future.” [VS]
Original Publication:
Kaufmann A., V. Beier, H. G. Franquelim and Wollert T., Molecular Mechanism of Autophagic Membrane-Scaffold Assembly and Disassembly, Cell, January 30, 2014.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.022
Contact
Dr. Thomas Wollert
Molecular Membrane and Organelle Biology
Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry
Am Klopferspitz 18
82152 Martinsried
Germany
Email: wollert@biochem.mpg.de
www.biochem.mpg.de/wollert
Anja Konschak
Public Relations
Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry
Am Klopferspitz 18
82152 Martinsried
Germany
Tel. +49 89 8578-2824
E-Mail: konschak@biochem.mpg.de
www.biochem.mpg.de
Weitere Informationen:
http://www.biochem.mpg.de/en/news/pressroom
– Press Releases of Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry
http://www.biochem.mpg.de/en/rg/wollert
– Website of the Research Group “Molecular Membrane and Organell Biology”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.biochem.mpg.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



