Limb regeneration: Do salamanders hold the key?
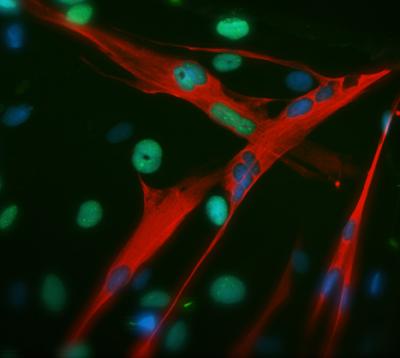
This is an image of differentiated salamander muscle cells re-entering the cell cycle, a crucial step for regeneration/reprogramming (cell nuclei -blue- that have re-entered the cell cycle are in green, while red labels differentiated muscle cells). Credit: UCL
For the first time, researchers have found that the 'ERK pathway' must be constantly active for salamander cells to be reprogrammed, and hence able to contribute to the regeneration of different body parts.
The team identified a key difference between the activity of this pathway in salamanders and mammals, which helps us to understand why humans can't regrow limbs and sheds light on how regeneration of human cells can be improved.
The study published in Stem Cell Reports today, demonstrates that the ERK pathway is not fully active in mammalian cells, but when forced to be constantly active, gives the cells more potential for reprogramming and regeneration. This could help researchers better understand diseases and design new therapies.
Lead researcher on the study, Dr Max Yun (UCL Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology) said: “While humans have limited regenerative abilities, other organisms, such as the salamander, are able to regenerate an impressive repertoire of complex structures including parts of their hearts, eyes, spinal cord, tails, and they are the only adult vertebrates able to regenerate full limbs.
We're thrilled to have found a critical molecular pathway, the ERK pathway, that determines whether an adult cell is able to be reprogrammed and help the regeneration processes. Manipulating this mechanism could contribute to therapies directed at enhancing regenerative potential of human cells.”
The ERK pathway is a way for proteins to communicate a signal from the surface of a cell to the nucleus which contains the cell's genetic material. Further research will focus on understanding how this important pathway is regulated during limb regeneration, and which other molecules are involved in the process.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



