New class of synthetic molecules mimics antibodies
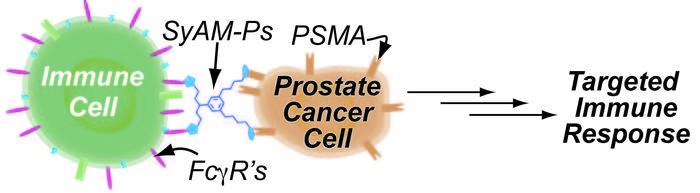
SyAMs recognize disease cells and bind with a specific protein on their surface. They also bind with a receptor on an immune cell. Credit: Yale University
The new molecules — synthetic antibody mimics (SyAMs) — attach themselves simultaneously to disease cells and disease-fighting cells. The result is a highly targeted immune response, similar to the action of natural human antibodies.
“Unlike antibodies, however, our molecules are synthetic organic compounds that are approximately one-twentieth the size of antibodies,” said David A. Spiegel, a professor of chemistry at Yale whose lab developed the molecules. “They are unlikely to cause unwanted immune reactions due to their structure, are thermally stable, and have the potential to be administered orally, just like traditional, small-molecule drugs.”
Spiegel and his team describe the research in a paper published online Dec. 16 by the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The paper looks specifically at SyAM molecules used to attack prostate cancer. Called SyAM-Ps, they work first by recognizing cancer cells and binding with a specific protein on their surface. Next, they also bind with a receptor on an immune cell. This induces a targeted response that leads to the destruction of the cancer cell.
Spiegel said the process of synthesizing and optimizing the structure of the molecules required considerable time and effort. “We now know that synthetic molecules of intermediate size possess perhaps the most important functional properties of antibodies — targeting and stimulation of immune cells,” he said.
“It's also noteworthy that molecules of such a small size can bring together two objects as enormous as cells, and trigger a specific functional response, entirely as a result of specific receptor interactions,” Spiegel added.
Beyond their potential for treating prostate cancer, SyAMs may have applications for treating other forms of cancer, HIV and various bacterial diseases.
Spiegel also is a member of Yale Cancer Center.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.yale.edu/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



