Discovery of Josephson Junctions Generated in Atomic-Layered Superconductors
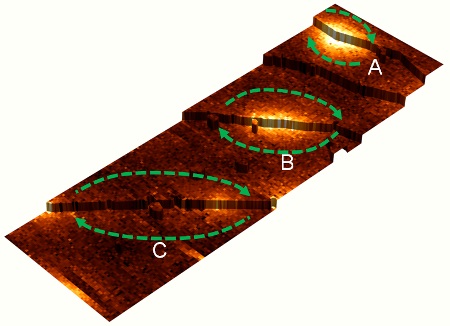
Figure 2 of the press release. A 3-D diagram of an atomic-layered superconductor observed under the scanning tunneling microscope. The heights of atomic layers are depicted, and the densities of localized electron states are represented by different brightnesses. Superconducting quantum vortices exist in the bright areas near atomic steps. The differences among A, B and C are attributed to the change in strength of the respective Josephson junctions, and to the differences in the gap width between the indium atomic layers near atomic steps. In particular, C is identified as a Josephson vortex. Arrows schematically indicate the flow of supercurrent and the pattern where, as a Josephson junction weakens, the vortex elongates in the direction parallel to the atomic step. Copyright : NIMS
A research group at the NIMS International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics and a research team at the Institute for Solid State Physics of the University of Tokyo discovered that in an atomic-scale-thick superconductor formed on a silicon surface, a single-atom difference in height between atomic layers (atomic step) acts as a Josephson junction that controls the flow of supercurrent. The results of this research have been published in the Physical Review Letters, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.247004.
(Shunsuke Yoshizawa, Howon Kim, Takuto Kawakami, Yuki Nagai, Tomonobu Nakayama, Xiao Hu, Yukio Hasegawa, and Takashi Uchihashi, Article title: “Imaging Josephson Vortices on the Surface Superconductor Si(111)−(√7×√3)−In using a Scanning Tunneling Microscope” Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 247004 – Published 10 December 2014.)
A research group at the NIMS (Sukekatsu Ushioda, president) International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics (MANA, Masakazu Aono, director), consisting of post-doctoral researcher Shunsuke Yoshizawa, MANA researcher Takashi Uchihashi, MANA principal investigator Tomonobu Nakayama, post-doctoral researcher Takuto Kawakami and MANA principal investigator Xiao Hu, and a research team at the Institute for Solid State Physics of the University of Tokyo, consisting of post-doctoral researcher Kim Howon and associate professor Yukio Hasegawa, discovered that in an atomic-scale thick superconductor formed on a silicon surface, a single-atom difference in height between atomic layers (atomic step) acts as a Josephson junction that controls the flow of supercurrent.
Recently discovered atomic-layered superconductors on a silicon surface have the potential of developing into ultra-tiny, superconducting nano-devices with atomic-scale thickness. However, fabrication of such devices requires the creation of a Josephson junction, an essential component in superconducting logic elements, and the method of creating such junctions had not been well understood.
Conducting an experiment using a scanning tunneling microscope, and performing microscopic theoretical calculations, the research team recently discovered that a special superconducting state called a Josephson vortex, a type of superconducting quantum vortex, is generated at atomic steps in atomic-layered superconductors. Based on this finding, the team revealed that atomic steps act as Josephson junctions. These results also indicate that the use of atomic-layered superconductors enables quick and mass fabrication of Josephson junctions in a self-organizing manner in contrast to the current method of fabricating the junctions one by one using conventional superconducting elements.
In consideration of these findings, in the future studies, the researchers are planning to fabricate Josephson elements that are only an atomic-level thick and apply them to superconducting devices. Also, it is known that Josephson vortices play a vital role in high-temperature superconductors that are a promising technology for electric power applications. The results from this study are expected to contribute to the identification of superconducting properties of high-temperature superconductors.
This study was jointly conducted with Yuki Nagai, a researcher at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, as a part of the world premier international research center initiative and the grants-in-aid for scientific research program sponsored by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
This study has been published in Physical Review Letters, an journal of the American Physical Society, as an Editors’ Suggestion article. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.247004
Associated links
NIMS press release
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.researchsea.comAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



