NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Nathan sporting hot towers, heavy rainfall
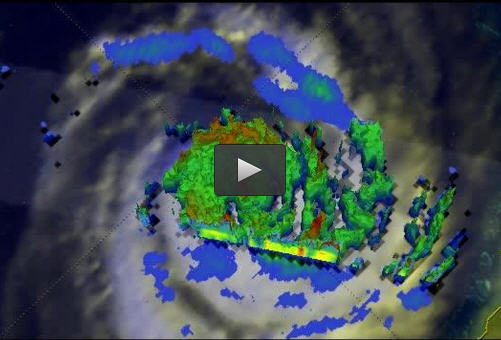
TRMM showed that the heaviest rainfall occurring in Nathan on March 18 at 0758 UTC (3:58 a.m. EDT) was falling at a rate of over 119 mm (4.7 inches) on the eastern side of Nathan's eye. TRMM Precipitation Radar data were used to create a 3-D view that showed storm heights of over 9.9 miles. Credit: NASA/JAXA/SSAI, Hal Pierce
Cyclone Nathan is located in the Coral Sea off Australia's Queensland coast. Nathan formed on March 10 near the Queensland coast triggering warnings there before moving east. Once out at sea, Nathan made a loop and headed back to Queensland.
On March 18, Nathan was nearing the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland. As a result warnings were in effect from Cape Melville to Innisfail, extending inland to Laura. Under watch is the area from Lockhart River to Cape Melville, extending inland to areas including Palmerville.
NASA-JAXA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite showed that the heaviest rainfall occurring in Tropical Cyclone Nathan on March 18 at 0758 UTC (3:58 a.m. EDT) was falling at a rate of over 119 mm (4.7 inches) on the eastern side of Nathan's eye.
At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, TRMM Precipitation Radar data were used to create a 3-D view of cyclone Nathan that showed storm heights in a rain band circling the storm's northwestern side reached heights of over 16 km (9.9 miles). Those data also showed “hot towers” or storm tops in Nathan's eyewall were reaching heights of over 13 km (8 miles).
“A “hot tower” is a tall cumulonimbus cloud that reaches at least to the top of the troposphere, the lowest layer of the atmosphere. It extends approximately nine miles (14.5 km) high in the tropics. These towers are called “hot” because they rise to such altitude due to the large amount of latent heat. Water vapor releases this latent heat as it condenses into liquid. NASA research shows that a tropical cyclone with a hot tower in its eyewall was twice as likely to intensify within six or more hours, than a cyclone that lacked a hot tower.
On Mar. 18 at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted that Nathan had reached hurricane force with maximum sustained winds near 65 knots (75 mph/120.4 kph). It was centered near 14.9 south latitude and 148.9 east longitude, about 225 nautical miles (258.9 miles/416.7 km) east-northeast of Cairns, Queensland, Australia. It was moving to the west at 2 knots (2.3 mph/3.7 kph) and generating wave heights to 22 feet (6.7 meters).
The MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Cyclone Nathan off the Queensland, Australia coast on March 18, 2015 at 04:15 UTC (12:15 a.m. EDT). The MODIS instrument showed a pinhole eye, about 5 nautical miles (5.7 miles/9.2 km) wide.
JTWC forecasters noted that Nathan is moving into an area of warm sea surface temperatures that will allow the storm to strengthen before making landfall on the Cape York Peninsula. JTWC forecasts call for Nathan to strengthen to 85 knots (97.8 mph/157.4 kph) by March 19 at 0600 UTC (2 a.m. EDT). For updated warnings and forecasts from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, visit: http://www.
It is forecast to make landfall north of Cairns on March 19 (by 1800 UTC) and move in a west-northwesterly direction across the Cape York Peninsula and into the Gulf of Carpentaria.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



