NASA sees Tropical Cyclone 22S 'come together right now'
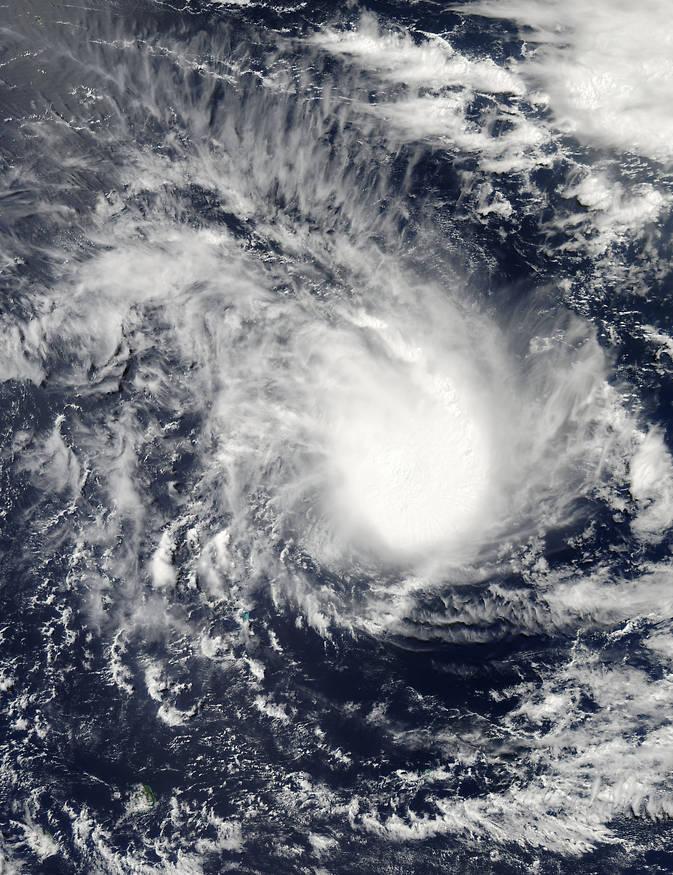
NASA's Aqua satellite captured this visible-light image of Tropical Storm 22S in the Southern India Ocean on April 6 at 09:45 UTC. Credit: NASA Goddard's MODIS Rapid Response Team
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm 22S as it organized and became a tropical storm on April 6 at 09:45 UTC (5:45 a.m. EDT).
The image was created by the NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team, at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
The image showed a rounded area of clouds associated with the tropical storm and a band of thunderstorms from the north feeding into the eastern side of the center of circulation.
On April 6, 2015, at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Tropical Cyclone 22S' maximum sustained winds were near 45 knots (51.7 mph/83.3 kph).
It was centered near 14.9 south latitude and 61.4 east longitude, about 401 nautical miles (461 miles/ 743 km) northeast of Port Louis, Mauritius. 22S has tracked west-southwestward at 9 knots (10.3 mph/16.6 kph).
22S is moving along the northern edge of a subtropical ridge (elongated area) of high pressure and once that ridge weakens and moves east, the tropical storm will turn to the south and intensify to hurricane-force upon approach to Rodrigues Island.
Rodrigues Island is an outer island in the Republic of Mauritius, located about 350 miles (560 km) east of Mauritius.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



