From Heart Attacks to Cancer: What Role Do Long, Non-Coding RNAs Play?
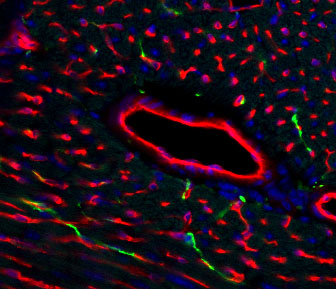
Blood vessels: An image of blood vessels in the heart (shown in red). The large vessel is surrounded by smaller vessels (capillaries). The nuclei are shown in blue, and the neurons are green. Dimmeler
Stefanie Dimmeler was one of the first researchers to prove that the sub-group of micro-RNAs plays a role in regenerating blood vessels. She has now received the coveted ERC Advanced Investigator Grant from the European Research Council (ERC), which will allow her to study another large group of non-coding RNAs. She believes that this group plays a role in creating heart attacks, strokes and cancer. ERC has awarded her 2.5 million Euros over the next five years.
“If you asked me what was special about the evolutionary development of human beings, I would say it´s the more than 30,000 non-coding RNA, most of which we only share with primates,” says Stefanie Dimmeler. From the perspective of her research area, cardiovascular regeneration, it is especially noteworthy that vascular illnesses like arteriosclerosis, which causes heart attacks, only occur in their typical form in humans.
There are many indicators that long, non-coding RNAs, lncRNAs for short, control these illnesses. They affect the inside layer of the blood vessels, known as endothelial cells, and help supply the organs and tissues with oxygen and nutrients.
The technologies used to track these lncRNAs and their complex functions are much more complicated than finding proteins. Dimmeler and her working group identified two candidates, Angiolnc1 and Angiolnc2, that regulate the functions of endothelial cells. Now she wants to study the molecular epigenetic mechanisms that these two lncRNAs use to trigger vascular illnesses. The goal of this research is to identify new treatments for preventing arteriosclerosis, in order to reduce the incidence of heart attacks and strokes.
In the third part of her project, Dimmeler will study whether ring-shaped lncRNAs, which have special protection once they are released into the blood, can be used as biomarkers for identifying illnesses in the vascular system or the heart. To this end, she will work with her group to develop tests that can be used to find these biomolecules in patients’ blood during the various stages of cardiovascular illnesses.
Prof. Stefanie Dimmeler, born in 1967, studied Biology at the University of Constance, where she received her doctorate in 1993. After two years as a research assistant at the University of Cologne, she went to Goethe University, where she was promoted to professor in 1998 in the Department of Experimental Medicine. In 2001, she accepted a position as a professor in the Molecular Cardiology Department at Goethe University. She has been the Director of the Institute of Cardiovascular Regeneration, in the Center for Molecular Medicine, since 2008.
She is the co-speaker of the DFG-funded “Cardiopulmonary Systems” Excellence Cluster, the “LOEWE Center for Cell and Genetic Therapy” funded by the State of Hesse, and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK) funded by the German Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) at the Rhine-Main site. She is a member of the Macromolecular Complexes Excellence Cluster as well as several specialized research areas. From 2008 to 2012, she was a member of the German Ethics Commission. Stefanie Dimmeler has received numerous research prizes, including the renowned Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize from the German Research Foundation and the Ernst Jung Prize for Medicine.
Information: Prof. Stefanie Dimmeler, Institute for Cardiovascular Regeneration, Niederrad Campus, Main Office: Claudia Herfurth, Tel.: +49(0)69) 6301-6667, herfurth@med.uni-frankfurt.de.
Goethe University is a research-oriented university in the European financial centre Frankfurt founded in 1914 with purely private funds by liberally-oriented Frankfurt citizens. It is dedicated to research and education under the motto “Science for Society” and to this day continues to function as a “citizens’ university”. Many of the early benefactors were Jewish. Over the past 100 years, Goethe University has done pioneering work in the social and sociological sciences, chemistry, quantum physics, brain research and labour law. It gained a unique level of autonomy on 1 January 2008 by returning to its historic roots as a privately funded university. Today, it is among the top ten in external funding and among the top three largest universities in Germany, with three clusters of excellence in medicine, life sciences and the humanities.
Publisher: The President of Goethe University, Marketing and Communications Department, 60629 Frankfurt am Main
Editor: Dr. Anke Sauter, Science Editor, International Communication, Tel: +49(0)69 798-12498, Fax +49(0)69 798-761 12531, sauter@pvw.uni-frankfurt.de
Internet: www.uni-frankfurt.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



