Discovery of a "heat-storage ceramic"
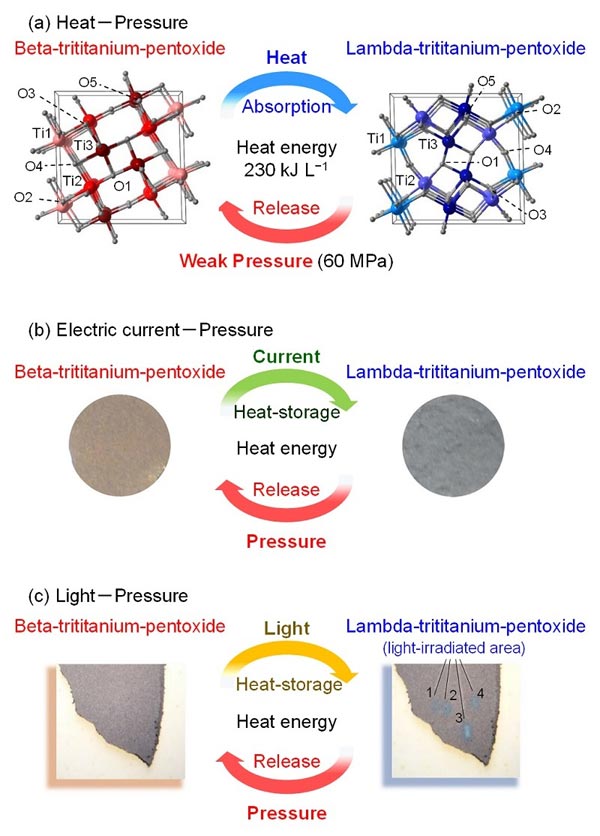
A novel “heat-storage ceramic” demonstrated in stripe-type-lambda-trititanium-pentoxide. (a) The material stores heat energy of 230 kJ L-1 by heating and releases the energy by a weak pressure (60 MPa). In addition, this material stores heat energy by various approaches such as (b) electric current flow or (c) light-irradiation. © 2015 Shin-ichi Ohkoshi.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have discovered a new type of material which stores heat energy for a prolonged period, which they have termed a “heat storage ceramic.”
This new material can be used as heat storage material for solar heat energy generation systems or efficient use of industrial heat waste, enabling recycling of heat energy, since the material releases the stored heat energy on demand by application of weak pressure.
Materials capable of storing heat include those such as bricks or concrete that slowly release the stored heat, and others such as water or ethylene glycol that take in heat when they transform from a solid to a liquid. However, none of these materials can store heat energy over a long period as they naturally release it slowly over time. A material that could store heat energy for a long time and release it at the exact timing desired would be a boon for the field of renewable energy.
The heat storage ceramic discovered by the research group of Professor Ohkoshi at the University of Tokyo Graduate School of Science preserves heat energy for a prolonged period. This material, called stripe-type-lambda-trititanium-pentoxide, is composed of only titanium atoms and oxygen atoms, and can absorb and release a large amount of heat energy (230 kJ L-1).
This heat energy stored is large at approximately 70% of the latent heat energy of water at its melting point. Additionally, applying a weak pressure of 60 MPa (mega Pascal) to stripe-type-lambda-trititanium-pentoxide induces a phase transition to beta-trititanium-pentoxide, releasing the stored heat energy.
Besides direct application of heat, heat energy can be stored by passing an electric current through the material or irradiating it with light, enabling the repeated absorption and release of heat energy by a variety of methods.
Stripe-type-lambda-trititanium-pentoxide is a simple titanium oxide composed of abundant elements and is environmentally friendly. The present heat-storage ceramic is expected to be a new candidate for use in solar heat power generation systems, which are actively promoted nowadays by European countries, and also for efficient use of industrial heat waste.
This material also has possibilities for use for advanced electronic devices such as pressure-sensitive sheets, reusable heating pads, pressure-sensitive conductivity sensors, electric current driven type resistance random access memory (ReRAM), and optical memory.
Paper
H. Tokoro, M. Yoshikiyo, K. Imoto, A. Namai, T. Nasu, K. Nakagawa, N. Ozaki, F. Hakoe, K. Tanaka, K. Chiba, R. Makiura, K. Prassides, and S. Ohkoshi, “External stimulation-controllable heat-storage ceramics”, Nature Communications 6, Article number:7037, 2015, doi: 10.1038/ncomms8037.
Associated links
UTokyo Research article
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



